Figure 3.
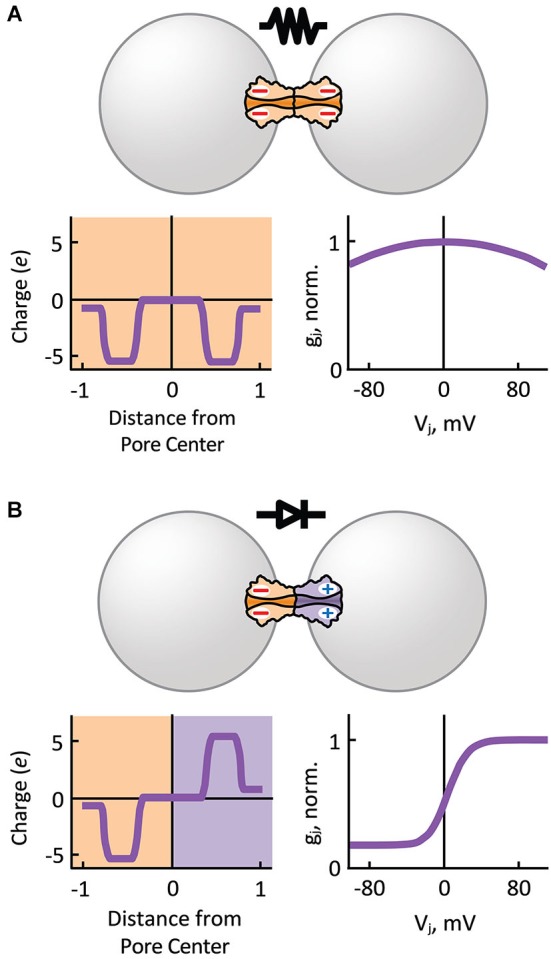
Hemichannel composition determines the symmetry of electrical transmission. (A) Homotypic gap junction channels that comprise symmetric charge distribution with respect to the pore center of the channel, behave as passive resistors with symmetric junctional conductance (gj) over transjunctional voltage (Vj) dependence (normalized to gj value at Vj equal zero). (B) Heterotypic gap junction channels that comprise an asymmetry in positive and negative charge distribution with respect to the pore center of the channel behave as electrical rectifiers (p-n junction) with steep asymmetric gj-Vj dependence. Normally, depolarizing (positive) potentials are more easily transmitted from the cell with negatively charged HCs to the cell with positively charged HCs.
