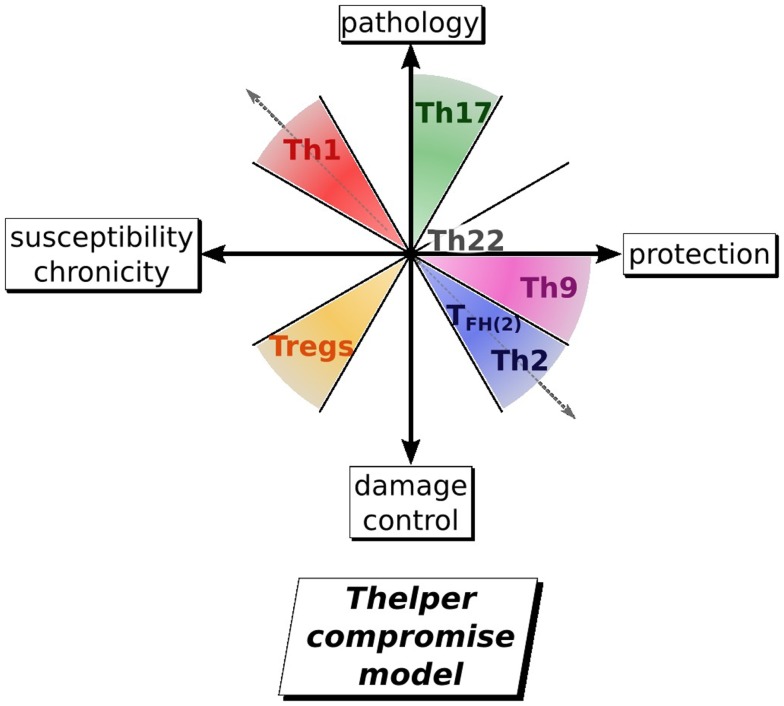
Figure 3.
Evolution of the view on T helper involvement in helminth infection. By taking into account all the other T helper subset known to date, it is proposed that an immune response against on helminth can be summarized as a 2D map defined by an axis of susceptibility/protection and an axis of pathology/damage control. For an optimal response against a parasite, the host would thus mount a Th2/Th9 response with a low Tregs response and almost not existing Th1, Th17 response. The Th2 arm of the immune response protects against helminth by expanding ILCs, eosinophils and basophils all involved in parasite expulsion or by activating macrophages in AAM, playing a role in granuloma formation. Th9 rather protects by increasing goblet cells hyperplasia and muscle contractility in the gut. Th17 induced pathology is mainly mediated by neutrophils and inflammatory macrophages. In contrary, Tregs induced development of regulatory macrophages, which control pathology.