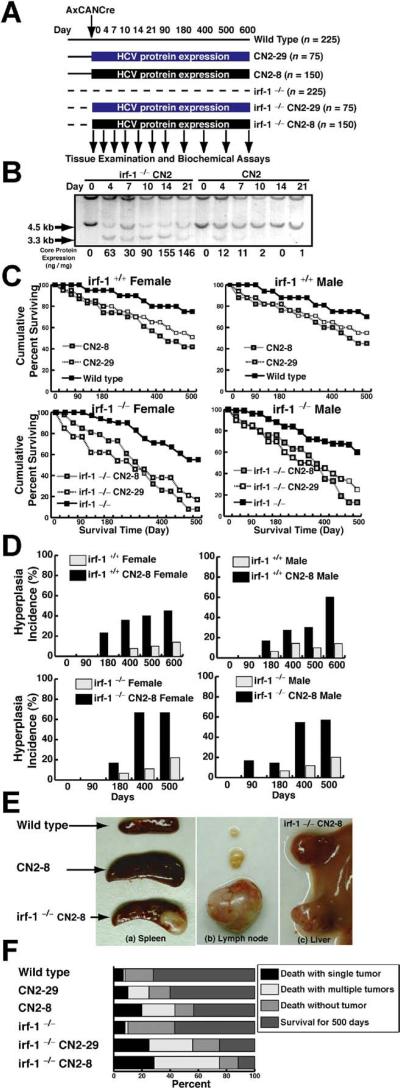
Figure 1.
Disruption of irf-1 enhances oncogenic potential in combination with HCV transgene expression. (A) Experimental design for the animal model. Transgenic mice and their nontransgenic littermates (10–14 weeks of age) were administered the Cre-expressing adenovirus (AxCANCre) and killed after 4, 7, 10, 14, 21, 90, 120, 400, 500, or 600 days. (B) Southern blot analysis of hepatocyte DNA from mice derived by crossing irf-1−/− and HCV-transgenic (CN2) mice. Genomic DNA samples from WT (+/+) and CN2 mouse hepatocytes were digested with XbaI and subjected to Southern blot analysis using a radio-labeled genomic flanking probe to determine the rate of recombination of the HCV transgene construct (3.3-kilobase fragment). Disruption of irf-1 allows persistent expression of HCV proteins. The effects of HCV protein expression on the survival rates of male and female irf-1−/− and irf-1+/+ CN2 mice are shown. (C) Kaplan–Meier survival curves for WT mice, irf-1−/− mice, CN2 transgenic mouse strains 8 and 29, and irf-1−/− CN2-8 and CN-29 mice following infection with a recombinant adenovirus that expresses cre (AxCANCre). (D) HCV protein expression enhances hyperplasia in male and female CN2 and irf-1−/− CN2 mice. The occurrence of hyperplasia was monitored every 7 days for 600 days following the administration of AxCANCre. (E) Spleens (a) and lymph nodes (b) from age-matched WT, CN2, and irf-1−/− CN2 mice 500 days after the administration of AxCANCre. (c) Liver from the same irf-1−/− CN2 mouse (developing severe lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly) following the administration of AxCANCre. (F) The cause of death in CN2 transgenic mice with hyperplasias. Mice of each genotype (n = 150) were monitored up to day 600 after the administration of AxCANCre, and necropsies were performed to determine the number of tumors. Tumors included thymomas, splenomas, lymphomas, and hepatocellular carcinomas.