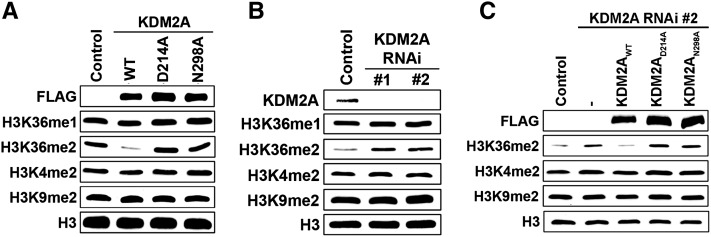
Figure 4.
Structure-guided mutations on KDM2A abolish its H3K36me2 demethylation activity in cells. (A) Overexpression of wild-type KDM2A, but not KDM2A carrying D214A or N298A mutations, reduces global H3K36me2 level in cells. Western analysis with the indicated antibodies of whole-cell extract (WCE) from 293T cells transfected with control vector, wild-type KDM2A, or catalytically inactive mutants. Total H3 is shown as loading control. (B) Depletion of KDM2A by RNAi increases global H3K36me2 level in cells. Western analysis as in A of whole-cell extract from HT1080 cells carrying control vector or stably expressing two independent RNAi targeting KDM2A transcript. (C) Complementation of KDM2A-depleted HT1080 cells with wild-type KDM2A, but not KDM2AD214A or KDM2AN298A, restores global H3K36me2 to the control level. Western analysis as in B of whole-cell extract from HT1080 control cells and KDM2A-depleted cells stably expressing KDM2AWT or catalytically inactive KDM2A.