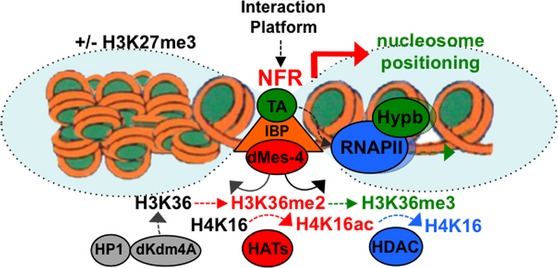
Model representing how the interactions of the IBP cofactor dMes-4 may regulate the expression of genes through the controlled accessibility of chromatin by H3K36me2-dependent recruitment of HATs for acetylation followed by H3K36me3-coupled nucleosome positioning and HDACs activation, closing back chromatin upon elongation of Pol II. Note that H3K36me3 is most likely coupled with transcription elongation upon activated by transcription activators (“TA”) such as DREF whose binding sites are highly enriched among DE genes regulated by dMes-4, as well as in “active” genes harboring high nucleosome positioning (Gilchrist
et al,
2010) (see Discussion). Note that H3K36 methylation levels in promoters further depend on the interaction of HP1 with the H3K36 demethylase dKdm4A as shown (Lin
et al,
2012) (see text).