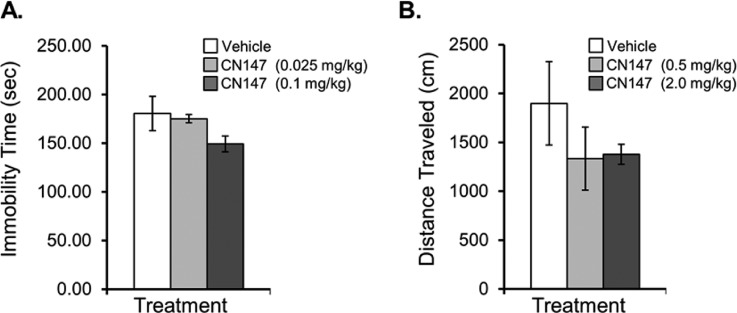
Figure 5.
Initial behavioral impact of the novel brain penetrant HDAC inhibitor, CN147. (A) Chronic (7 days) treatment with CN147 at 0.1 mg/kg resulted in a 17% reduction in forced-swim test immobility compared with vehicle-treated controls as evaluated by a trained scorer blinded to treatment groups. Treatment with CN147 at a lower dose (0.025 mg/kg) had no appreciable effect on FST immobility score compared with controls, and analysis by Spearman correlation revealed that CN147 dose and FST immobility times were significantly correlated (Spearman r = −0.0671, two-tailed p = 0.0192). (B) Locomotor effects of CN147 treatment were evaluated after 7 days treatment with 0.5 mg/kg or 2.0 mg/kg compared with vehicle-treated controls; distance traveled (cm) was lower in CN147-treated rats than in control animals and was not considered a confound to interpretation of decreased immobility observed in the forced-swim test. No treatment-group differences were observed in rat weight gain (data not shown).