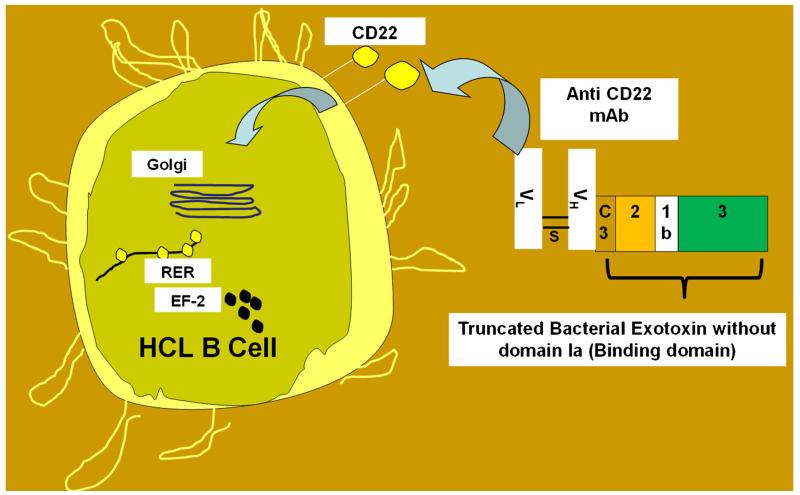
Fig. 2.
Structure and mechanism of action of immunotoxins in hairy cell leukemia (HCL). The binding domain of the bacterial exotoxin is replaced with the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) of the monoclonal antibody (in this case against CD22). After the internalization of the immunotoxin, the enzymatic domain (domain 3) ribosylates elongation factor 2 (EF-2) and inhibits protein synthesis. The affinity of the immunotoxins can be increased by mutations at CDR3 (third complementarity determining region), allowing higher binding of the immunotoxin to HCL cells.