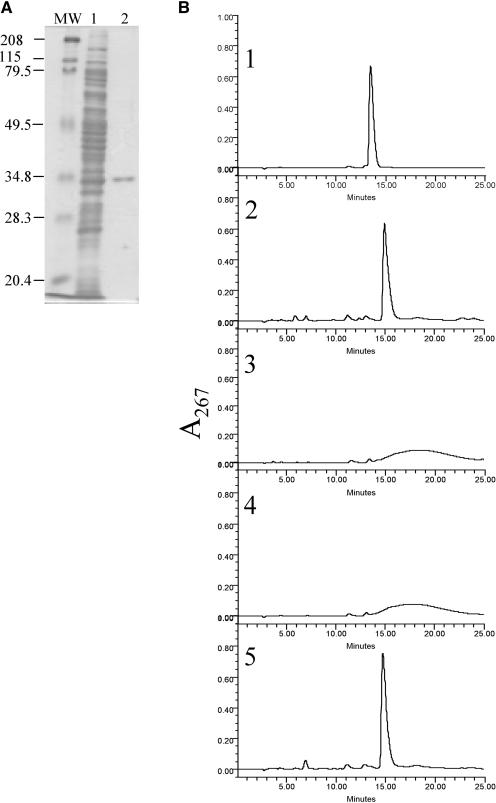
Figure 5.
Purification and determination of the enzymatic activity of NRS/ER. A, SDS-PAGE analysis of recombinant NRS/ER purified from E. coli: Lane MW, molecular weight marker proteins. Lane 1, total soluble protein from E. coli expressing NRS/ER. Lane 2, NRS/ER purified by Ni-affinity column chromatography. B, NRS/ER encodes a bifunctional epimerase/reductase that converts dTDP-4-keto-6-deoxy-Glc to dTDP-β-l-Rha. 1, The elution profile of dTDP-α-d-Glc on a ODS2-HPLC column. 2, dTDP-β-l-Rha was generated by incubating dTDP-α-d-Glc with the recombinant rmlB, rmlC, and rmlD proteins in the presence of NADPH. 3, dTDP-4-keto-6-deoxy-Glc was generated by incubating dTDP-α-d-Glc with the recombinant rmlB protein alone. The dTDP-4-keto-6-deoxy-Glc eluted as a broad peak from ODS2 column as previously reported (Nakano et al., 2000). 4, Purified NRS/ER was incubated with dTDP-4-keto-6-deoxy-Glc in the absence of NADPH. 5, Purified NRS/ER incubated with dTDP-4-keto-6-deoxy-Glc in the presence of NADPH to yield dTDP-β-l-Rha.