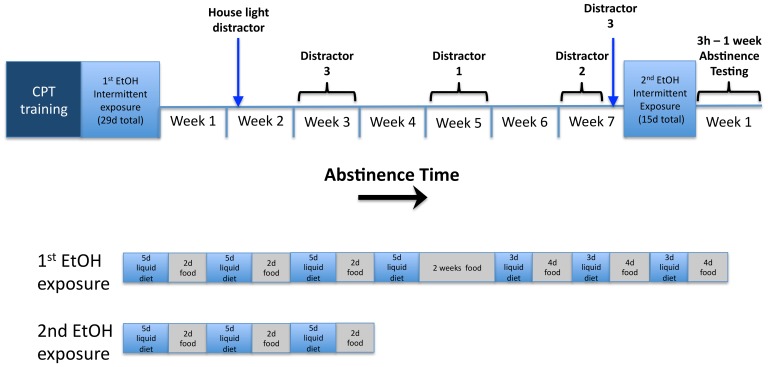
Figure 1. Experimental design.
Following 5C-CPT training, animals were given intermittent access to either an EtOH-containing (10% w/v) or EtOH-free control liquid diet over the course of 9 weeks (“1st EtOH exposure”, detailed in bottom panel; total of 29 days on liquid diet; average daily EtOH intake of 8.73±0.2 g/kg/day resulting in 210±14 mg% blood alcohol levels). 5C-CPT evaluations were performed during a subsequent 7-week abstinence period with visual distractor “challenge” tests performed during the 3rd, 5th and 7th week of abstinence to increase task difficulty in an effort to unveil EtOH-related cognitive impairment (see text for details of each distractor condition). EtOH-related disruptions in 5C-CPT performance during the first week of abstinence (3h – 5d) were evaluated following a second regimen of liquid diet exposure (“2nd EtOH exposure”, detailed in bottom panel; 15d intermittent access over 3 weeks; average daily EtOH intake of 8.83±0.7 g/kg/day resulting in 289±12 mg% blood alcohol levels).