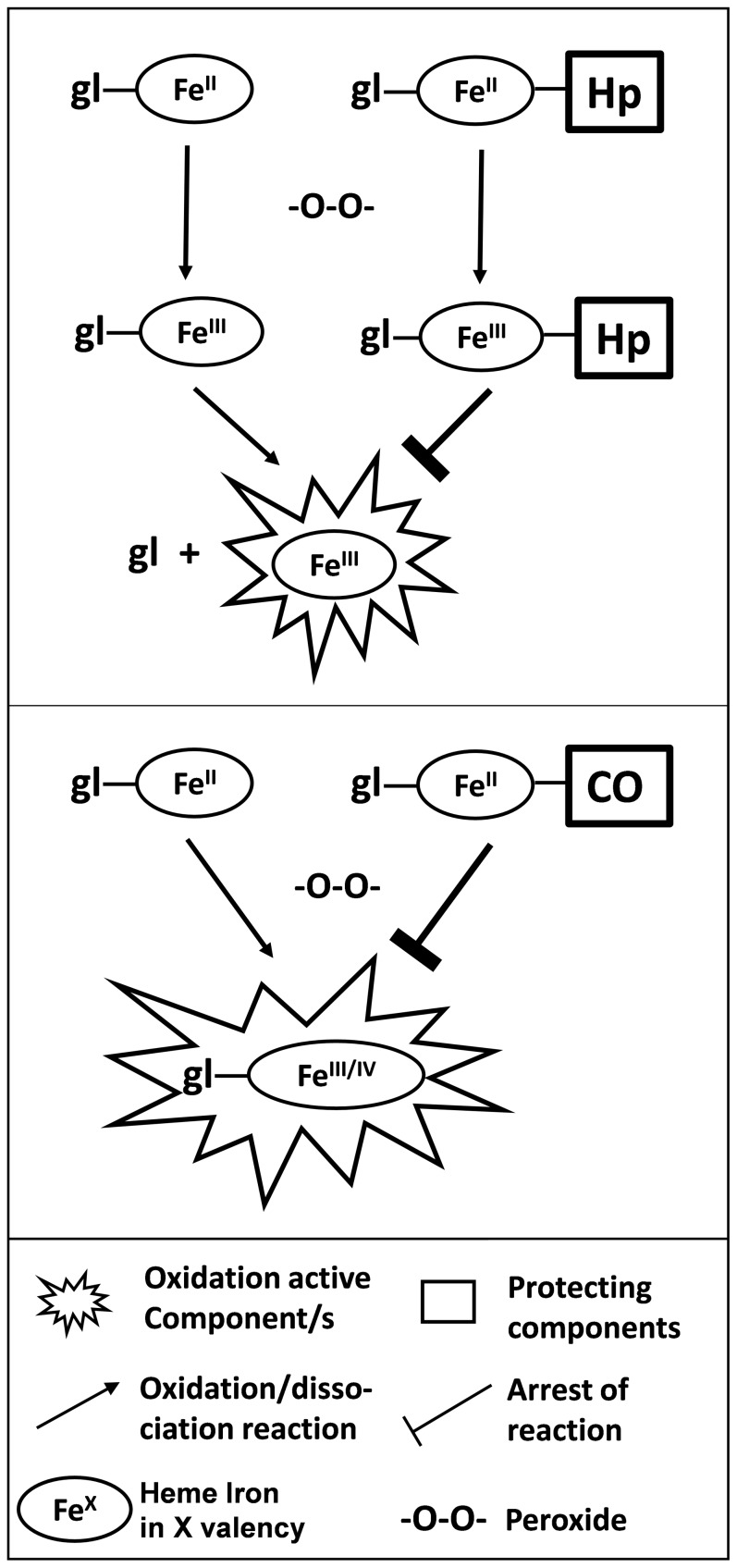
Figure 9. Differences in Hb and Mb induced oxidation yield distinct protection mechanisms.
In presence of peroxide, ferrous RH are oxidized to their ferric (FeIII) and/or ferryl (FeIV) forms. Upper: Hp binds Hb (ferrous and/or ferric) thereby preventing its release. Lower: Mb heme is retained attached to globin following oxidation in a peroxidase-like form. However, binding of CO to ferrous Mb prevents its oxidation to a ‘peroxidase-like form”.