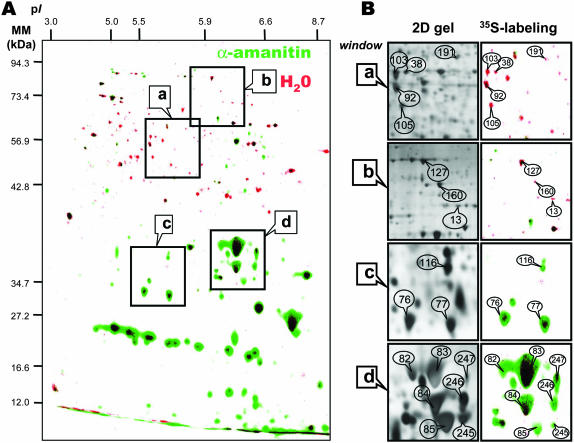
Figure 7.
Comparison of de novo protein synthesis patterns during 24-h germination of the tt2-1 Arabidopsis mutant in the presence or absence of α-amanitin. The data are from Figure 6. Seeds were incubated for 24 h in the presence of [35S]Met, in the absence or presence of 500 μm α-amanitin. Proteins were extracted, submitted to 2D gel electrophoresis, and the radiolabeled proteins revealed as described in “Materials and Methods.” A, Superimposition of the two labeled protein patterns shown in Figure 6A and B. The data are represented in false colors: Red, incubation in water (Fig. 6A); Green, incubation in α-amanitin (Fig. 6B). The indicated portions of the gel, a, b, c, and d, are reproduced in B. B (right; 35S-labeling), Enlarged windows a, b, c, and d of 2D gels as shown in A for tt2-1 dry mature seeds incubated in water for 24 h (red spots) or in the presence of 500 μm α-amanitin (green spots). B (left; 2D gel), Same enlarged windows (a–d) of a 2D gel of proteins extracted from tt2-1 dry mature seeds incubated in water for 24 h and revealed by silver nitrate coloration. The labeled protein spots were identified by comparison with Arabidopsis seed protein reference maps (Gallardo et al., 2001, 2002a, http://seed.proteome.free.fr). They are listed in Tables III and IV. The following spots are shown in the four selected windows (protein no., protein name). Window (a): 103, enolase; 38, Leu aminopeptidase; 92, myrosinase-binding protein; 105, elongation factor1-γ2; 191, mitochondrial processing protease. Window (b): 127, elongation factor EF-2; 160, Met synthase; 13, MLO-like protein. Window (c): 116, P1 clone:MRA19, strong similarity to unknown protein T05029; 76 and 77, α-cruciferin 12S seed storage protein (fragments). Window (d): 82, 83, 84, 85 and 245, α-cruciferin 12S seed storage protein (fragments); 246, globulin seed storage protein precursor (fragment); 247, hydrolase.