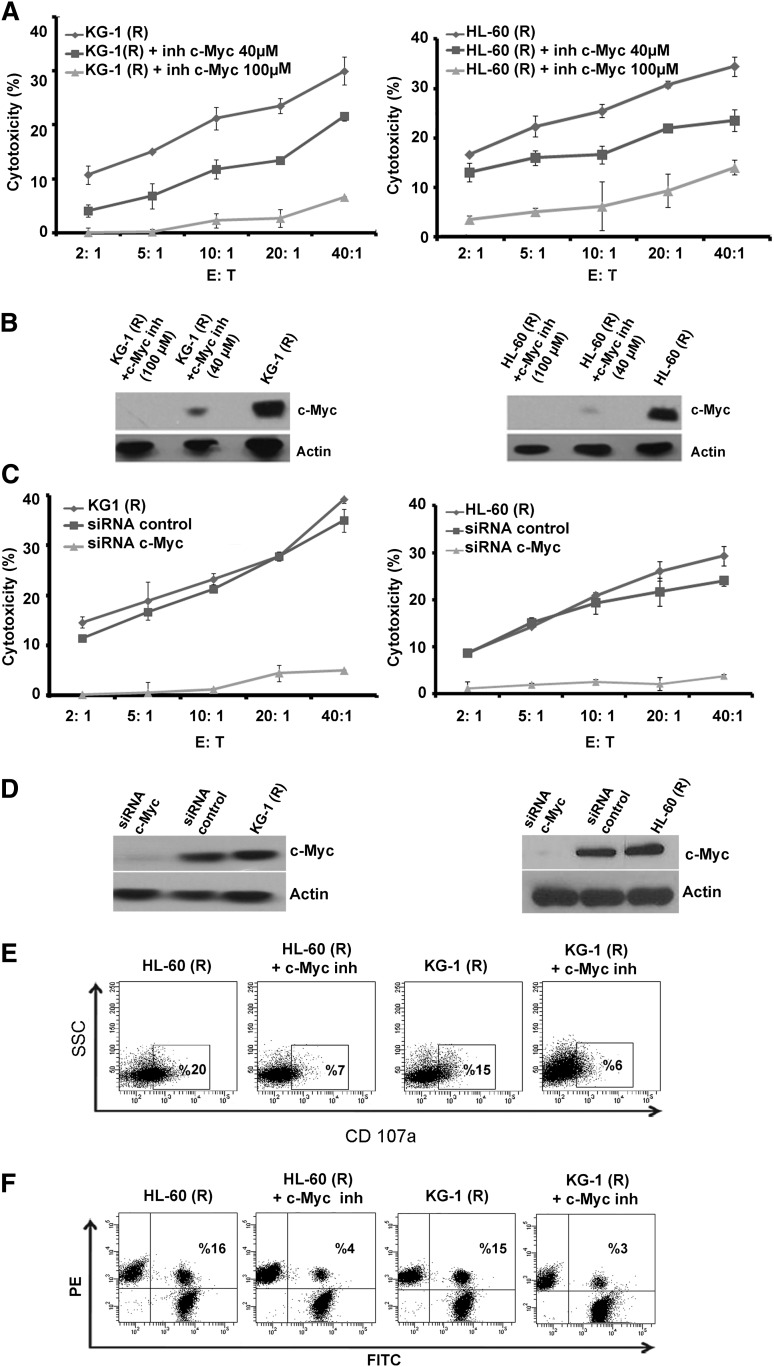
Figure 5.
Effect of c-Myc inhibition on NK-cell–mediated killing of cytarabine-resistant cells. (A) NK-cell cytotoxicity of KG-1(R) and HL-60(R) cells after incubation with 10058-F4 (40 µM and 100 µM) for 24 hours. (B) Experimental values were determined by western blot analysis using anti–c-Myc antibody. Actin was used as the protein level control. (C) NK-cell cytotoxicity of KG-1(R) and Hl-60(R) cells after inhibition of c-Myc by specific siRNA or a negative control siRNA (Luc). (D) Transfection efficiency was determined by western blot analysis using anti–c-Myc antibody. Actin was used as the protein level control. (E) Flow cytometric analysis of CD107a expression on NK cells cocultured for 4 hours with KG-1(R) and HL-60(R) with or without 10058-F4 (100 µM for 24 hours) at E:T ratio of 2:1 (representative blot of n = 3). (F) Conjugate formation assay between NK cells and KG-1(R) and HL-60(R) with or without 10058-F4 (100 µM for 24 hours) at E:T ratio of 2:1 (representative blot of n = 3).