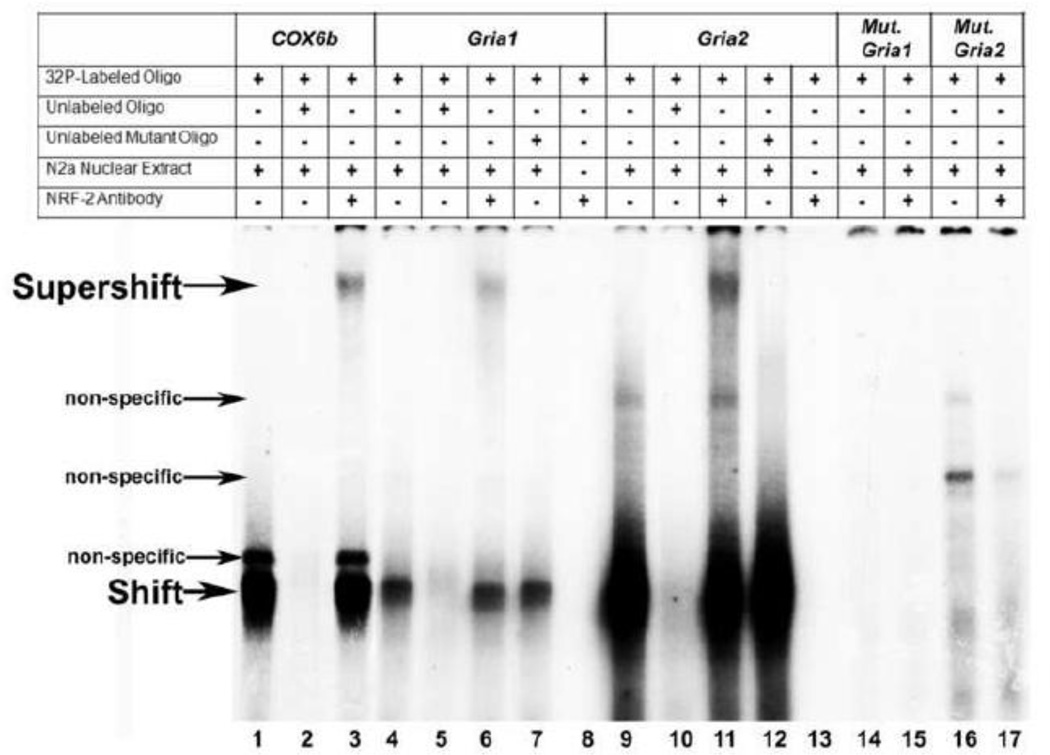
Figure 1.
In vitro binding of NRF-2 to putative binding sites on the AMPA receptor subunit gene promoters as determined with EMSA and supershift assays. 32P-labeled oligonucleotides, excess unlabeled oligos as competitors, excess unlabeled mutant NRF-2 oligos as competitors, N2a nuclear extract, and NRF-2α antibodies are indicated by a + or a − sign. Arrowheads indicate specific NRF-2 shift, supershift, and non-specific complexes. The positive control, COX6b, shows a shift and supershift band (lanes 1 and 3, respectively). The addition of excess unlabeled probe competed out the shift band (lane 2). The addition of N2a nuclear extract yielded specific shift bands for both Gria1 and Gria2 (lanes 4 and 9, respectively) that were competed out by an excess of unlabeled oligos (lanes 5 and 10, respectively). The addition of NRF-2 antibody yielded a supershift band for both Gria1 and Gria2 (lanes 6 and 11, respectively). The addition of excess unlabeled probes with mutated NRF-2 binding sites did not compete out the shift reaction (lanes 7 and 12, respectively). The addition of NRF-2 antibody to labeled Gria1 and Gria2 probes in the absence of N2a extract did not reveal any antibody-to-probe reaction (lanes 8 and 13, respectively). Labeled Gria1 and Gria2 probes with mutated NRF-2 sites did not yield a specific NRF-2 shift band (lanes 14 and 16, respectively), nor a supershift band with the addition of NRF-2 antibody (lanes 15 and 17, respectively).