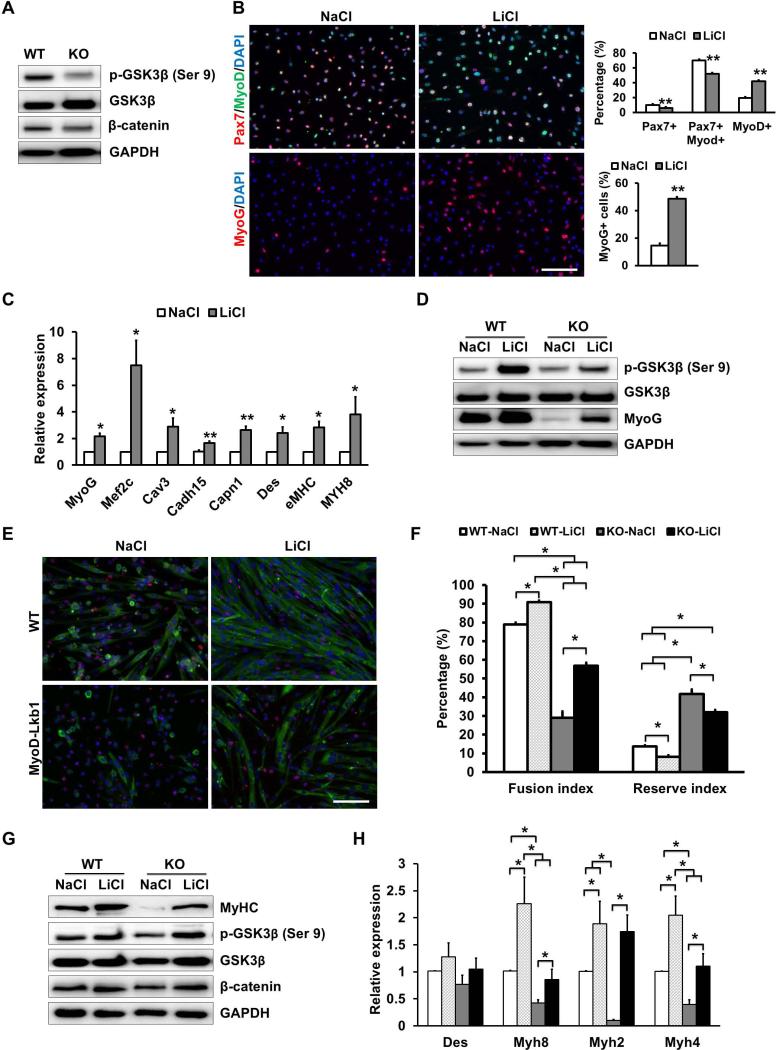
Figure 7.
Lkb1 acts through GSK3β to regulate myogenic differentiation. (A) Relative protein levels of phosphorylated GSK3β (pGSK3β, Ser9) and β-catenin expression in WT and MyoDLkb1 myoblasts. (B) Morphology and percentage of quiescent (Pax7+MyoD-) and proliferating (Pax7+MyoD+) and differentiating (Pax7-MyoD+ or MyoG+) myoblasts treated with a GSK3β inhibitor (LiCl, 20 mM) or control (NaCl, 20 mM) media. (C) Expression of differentiation and fusion related genes after LiCl treatment. (D) LiCl rescued pGSK3 β and MyoG expression in MyoD-Lkb1 myoblasts. (E) MF20 staining (Red) showing differentiation efficiency of WT and MyoD-Lkb1 myoblasts cultures with or without LiCl. Scale bars: 100 μm. (F) LiCl partially rescued the differentiation efficiency (fusion index) of MyoD-Lkb1 myoblasts. (G-H) LiCl rescued the expression of differentiation marker genes in Lkb1 null myotubes. Error bars represent SEM, n=5. P< 0.05 between bars labeled by different letters (a, b, c and d), * means P< 0.05, ** P< 0.01.