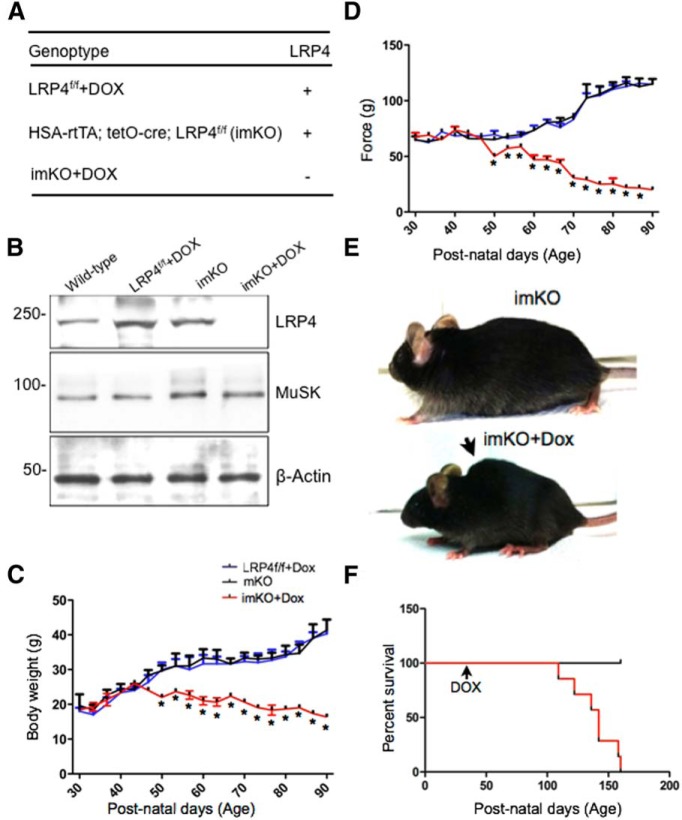
Figure 1.
LRP4 is depleted from NMJs following conditional deletion in adults. A, Genotypes and LRP4 deletion in skeletal muscle. In ACTA1-rtTA; tetO-cre transgenic mice (Rao and Monks, 2009), cre is expressed under control of the ACTA1 (human actin α1, skeletal muscle) promoter, whereas cre expression is controlled by tetracycline inducible element (tetO). The bitransgenic mice do not express Cre until doxycycline is administered. ACTA1-rtTA; tetO-cre mice were bred with LRP4f/f mice (Wu et al., 2012b) to generate ACTA1-rtTA; tetO-cre; LRP4f/f (imKO). Dox-treated imKO mice did not express LRP4. Unless otherwise specified, LRP4f/f mice were used as control. B, Reduction of LRP4 in Dox-treated imKO mice. Tibialis anterior muscle was isolated from mice of indicated genotypes and treatment and blotted for LRP4, MuSK, and β-actin. C, Dox-treated imKO mice progressively lost weight, compared with imKO or LRP4f/f+DOX mice; n = 3 per genotype (two-way ANOVA). *p < 0.05 (Student's t test). D, Decreased grip strength in Dox-treated imKO mice; n = 3 per genotype (two-way ANOVA). *p < 0.05 (Student's t test). E, Dox-treated imKO mice were considerably smaller in size, compared with imKO mice, and developed scoliosis after 30 d of Dox treatment. F, Kaplan–Meier survival curves of control and Dox-treated imKO mice. χ2 = 22.67, p < 0.0001 (Log-Rank; Mantel–Cox test).