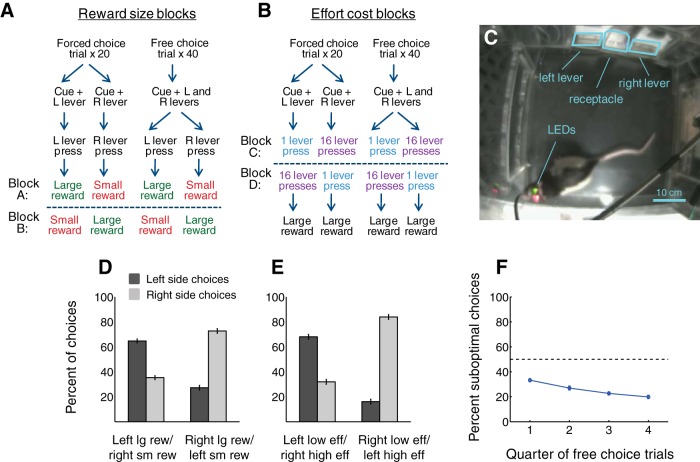
Figure 1.
Task and behavior. A, B, Sequence of events during a decision-making task in which reward size (A) and effort cost (B) were systematically varied. In Block A, a left lever press resulted in the availability of a large reward and a right lever press resulted in the availability of a small reward. In Block B, these contingencies were reversed. In Blocks C and D, the effort level required to obtain reward was varied in a similar manner, but reward size was held constant. The four blocks were presented in pseudo-random order during different sessions, but Blocks A and B were always presented back-to-back, as were Blocks C and D. C, Rat in behavioral chamber. The rat's movements were recorded using video tracking software and two head-mounted LEDs. D, E, Average behavioral performance during Blocks A and B (D) and Blocks C and D (E) over 45 sessions. Error bars indicate SEM. F, Probability of suboptimal choices over the course of 40 free choice trials, averaged over 45 sessions. Error bars indicate SEM.