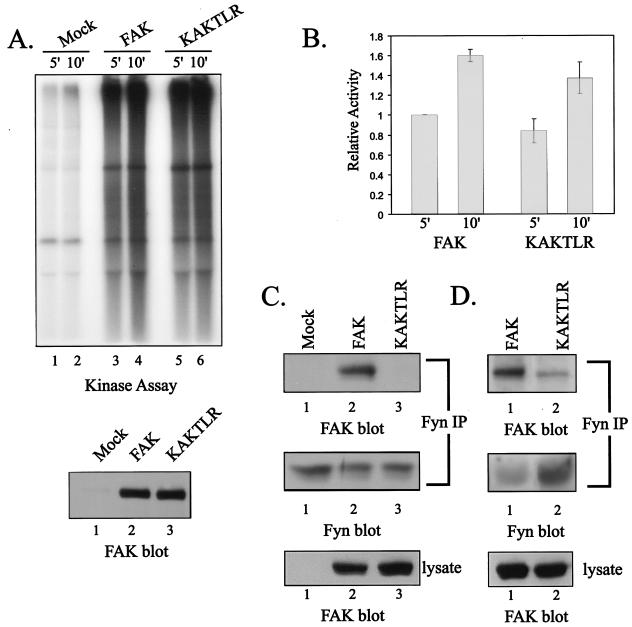
FIG. 7.
KAKTLR is catalytically active but is defective for Fyn binding. (A) Endogenous FAK (lanes 1 and 2) and exogenously expressed wild-type FAK (lanes 3 and 4) or KAKTLR (lanes 5 and 6) were immunoprecipitated from CE cell lysates, and the immune complexes were incubated in an in vitro kinase assay with poly(Glu,Tyr) for 5 or 10 min (top panel). A fraction of each immune complex was also blotted for FAK to verify equal recovery of wild-type FAK (lane 2) and KAKTLR (lane 3) (bottom panel). (B) The results from five experiments were quantified by phosphorimager analysis. Phosphorylation of substrate following 5 min incubation with FAK was arbitrarily set as 1. The error bars indicate standard errors. (C) CE lysates containing empty vector (lanes 1) or expressing FAK (lanes 2) or KAKTLR (lanes 3) were used for immunoprecipitations (IP) with a Fyn polyclonal antiserum. The immune complexes were blotted with BC4 to detect coimmunoprecipitated FAK (top panel), and then the blot was stripped and reprobed for Fyn (middle panel) to demonstrate equal recovery of Fyn in the immunoprecipitations. Expression of wild-type and mutant FAK was compared by blotting 25 μg of cell lysate with BC4 (bottom panel). (D) Fyn was immunoprecipitated from lysates of FAK (lanes 1)- or KAKTLR (lanes 2)-overexpressing cells following adhesion to fibronectin-coated plates for 20 min. Immune complexes were analyzed by Western blotting with BC4 (top panel), and the blots were stripped and reprobed for Fyn (middle panel). Expression of wild-type and mutant FAK was compared by blotting 25 μg of cell lysate with BC4 (bottom panel).