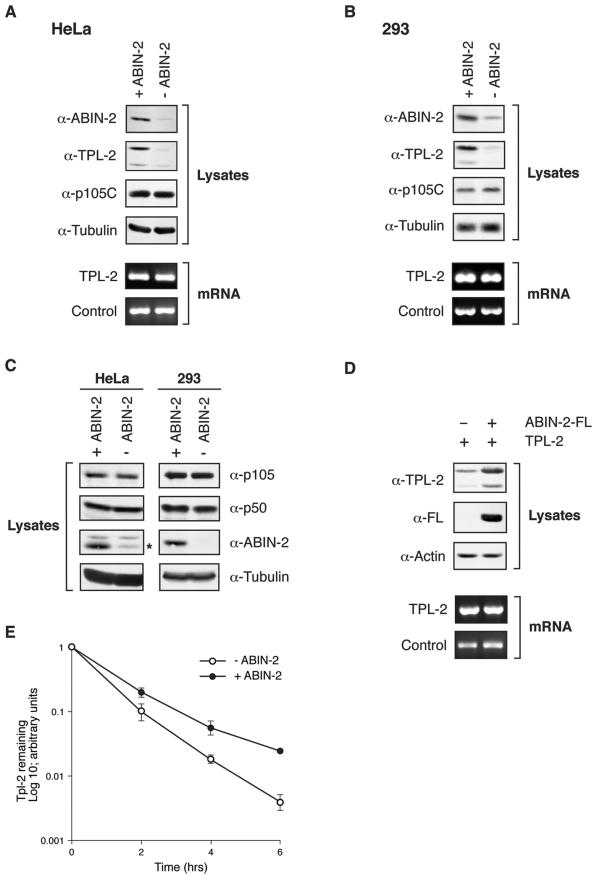
FIG. 7.
Depletion of ABIN-2 by RNA interference dramatically reduces steady-state levels of TPL-2. (A and B) ABIN-2 expression in HeLa S3 cells (A) and 293 cells (B) was decreased by siRNA treatment (−ABIN-2). Control cells were treated with an irrelevant siRNA oligonucleotide pair (+ABIN-2). Cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE (10% acrylamide) and Western blotting (top blots). TPL-2 mRNA levels in total RNA were assayed by semiquantitative RT-PCR (bottom blots). The 18S rRNA amplicon was used as an internal control. α, anti. (C) ABIN-2 was depleted by RNA interference in HeLa and 293 cells as described above for panels A and B. Expression of p105, p50, or ABIN-2 was determined by Western blotting of cell lysates. The position of the ABIN-2 band in the Western blot of HeLa cell lysates is indicated by an asterisk. (D) 293 cells were cotransfected with vectors encoding TPL-2 and ABIN-2-FL or with EV. Lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE (10% acrylamide) and Western blotting (top blots). In duplicate cultures, transfected TPL-2 mRNA levels were determined by semiquantitative RT-PCR (bottom blots). 18S rRNA was used as an internal control. (E) 293 cells were cotransfected with expression vectors encoding TPL-2 and ABIN-2-FL or with EV. After 24 h, cells were metabolically pulse-labeled with [35S]methionine-[35S]cysteine (30 min) and then chased for the times indicated. Anti-TPL-2 immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS-PAGE (8% acrylamide) and visualized by fluorography. Amounts of immunoprecipitated labeled TPL-2 were quantified by densitometry (n = 3).