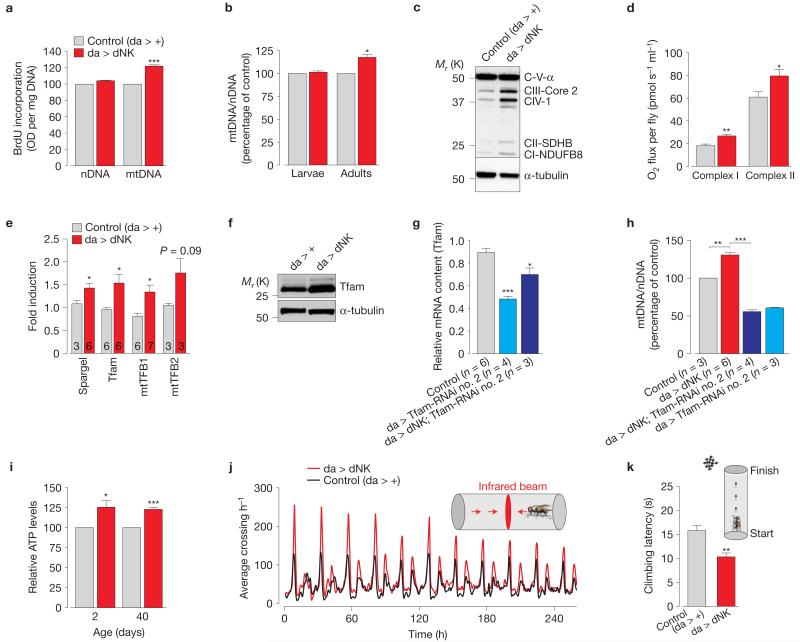
Figure 2. dNK enhances mitochondrial function by promoting organellar biogenesis.
(a) Enhanced mtDNA synthesis in dNK transgenic flies. DNA synthesis was assessed using a BrdU assay (mean±s.e.m.; n = 12; asterisks, two-tailed paired t-test). (b) dNK flies show an increase in mtDNA. The ratio of mtDNA to nuclear DNA (nDNA) was measured by real-time PCR using third-instar larvae and 2-day-old flies with the indicated genotypes (mean±s.d.; n = 9; asterisks, two-tailed paired t-test). (c) dNK flies show an increase in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation proteins. Immunoblot of samples prepared from whole 2-day-old males. α-tubulin, loading control. (d) Enhanced respiration in dNK flies. Data are shown as the mean±s.d. (n = 3 per genotype; asterisks, two-tailed unpaired t-test). (e) dNK flies show a transcriptional upregulation of the PGC-1 family homologue Spargel and the nuclear-encoded mtDNA binding proteins Tfam, mtTFB1 and mtTFB2. Data are shown as the mean±s.e.m. (n values are indicated in the bars; asterisks, two-tailed unpaired t-test). (f) dNK expression increases protein levels of mtTFA. Lysates prepared from adult flies were subjected to western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. (g) RNAi-mediated suppression of Tfam. Expression levels were measured by real-time PCR (relative mean Ct±s.e.m., n values are indicated). Statistically significant values relative to the control are indicated (one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test). (h) Tfam is required for the dNK-mediated increase in mtDNA. The ratio of mtDNA to nDNA was measured by real-time PCR using 2-day-old flies with the indicated genotypes (mean±s.e.m.; n values are indicated; asterisks, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test, *** P < 0.0001). (i) dNK expression results in a generalized ATP increase in both young (2-day-old) and old (40-day-old) flies. Data are shown as the mean±s.d. from three independent experiments (n = 3 per genotype; asterisks, two-tailed paired t-test). (j) Ubiquitous expression of dNK enhances locomotor activity. Sixteen flies were tested for each genotype. (k) Ubiquitous expression of dNK enhances climbing ability. Flies were tested using a standard climbing assay (mean±s.e.m.; n = 100 flies per genotype; asterisks, two-tailed unpaired t-test). See also Supplementary Figs 2 and 9 and Table 9 for statistics source data of d,e,g-i.