Figure 1.
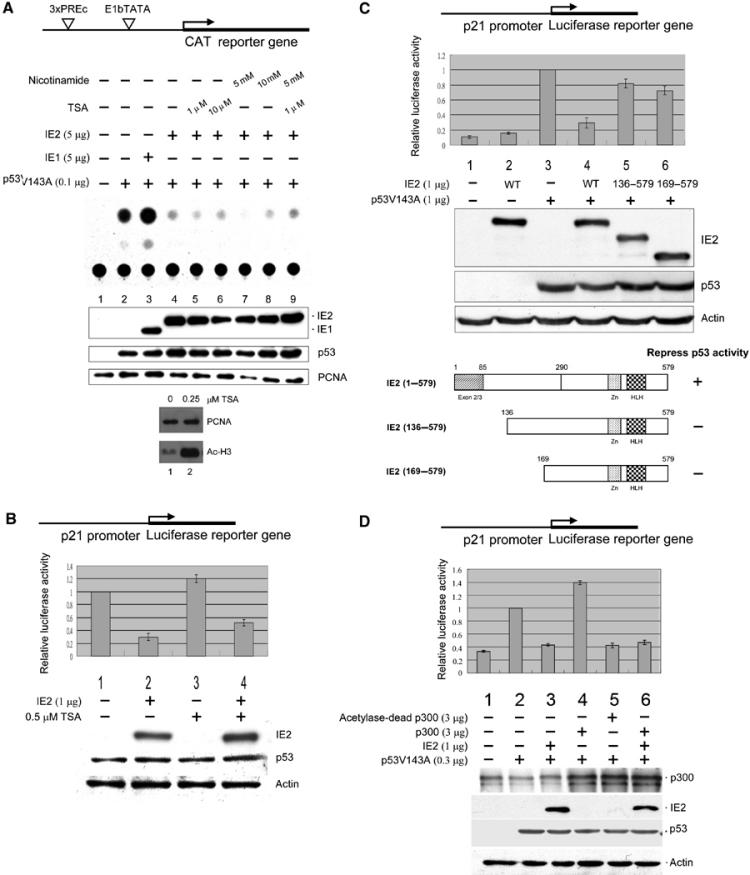
HCMV IE2-mediated suppression of p53-dependent gene activity. Cells were transfected with indicated expression plasmids, followed by CAT reporter assays (A) or luciferase assays (B–D) and Western analyses. The reporter constructs used are shown at the top of each figure. (A) IE2 inhibits p53-specific gene activation by a TSA-insensitive mechanism. Upper panel: Autoradiogram of the TLC separation. The experiment was repeated three times giving means and standard errors of 0.13±0.02, 1.00±0, 1.60±0.16, 0.46±0.06, 0.32±0.02, 0.39±0.02, 0.35±0.02, 0.4±0.03, and 0.32±0.06 for lanes 1–9, respectively. Bottom panel: Cells were incubated for 12 h with or without 0.25 μM TSA, followed by Western analyses. PCNA: internal control. (B) IE2 downregulates endogenous p53-mediated activation of the p21 promoter. Upper panel: Firefly luciferase activity (p21-Luc) normalized to that of the Renilla luciferase (pRL-SV40) control. Bottom panel: Western blots, with actin as the internal control. (C) IE2 deletion mutants lacking the N-terminal 135 amino acids lost p53 inhibition activity. The WT or IE2 deletion mutants are shown in the bottom panel. IE2 (1–579) is full-length IE2, while IE2 (136–579) and IE2 (169–579) lack the N-terminal 135 or 165 residues, respectively. Residues 1–85 are the common region shared by IE1 and IE2. Zn: Zn finger domain; HLH: helix–loop–helix motif. (D) IE2 inhibits p300-mediated induction of p53 activity. The reporters used in (B–D) were 10 ng of p21-Luc and 10 ng of pRL-SV40, as an internal control. The antibodies for the Western blots were directed against the N-terminal 85 amino acids common to HCMV IE1 and IE2 (MAb810, Chemicon) (A), IE2 (polyclonal, see Materials and methods) (B–D), p53 (Ab-6, Oncogene), proliferation cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) (SC56, Santa Cruz), acetylated histone H3 (06-599, Upstate), actin (MAB1501, Chemicon), and p300 (NA-46, Oncogene).
