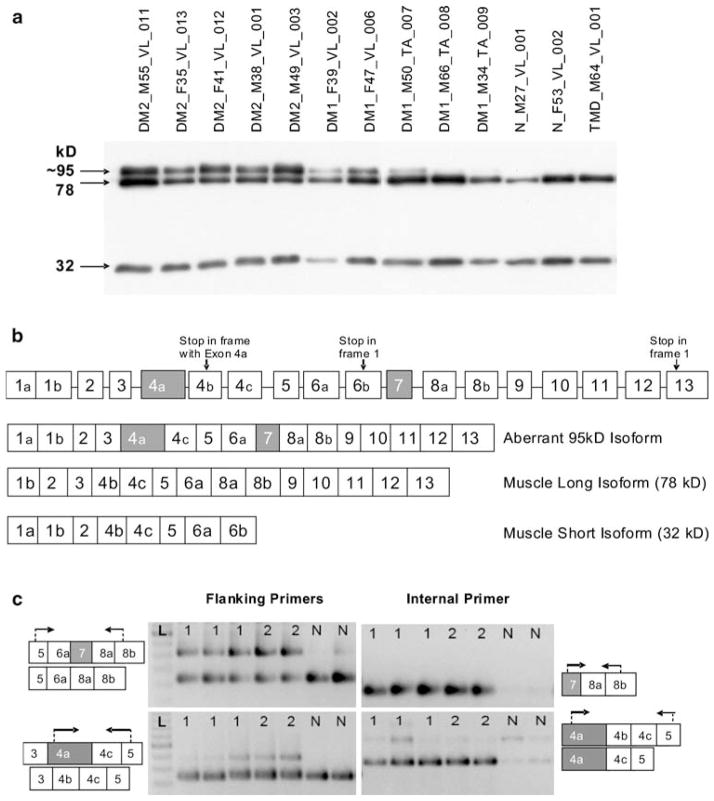
Fig. 4.
LBD3/ZASP expression. a Western blot of ZASP using samples identical to Fig. 3d. ZASP isoforms of 78 and 32 kD are present in all samples, while a strong band of ~95 kD is seen in all DM2 samples and three DM1 samples but not in the controls. The size of this band is consistent with the simultaneous inclusion of both cardiac exons in the protein (see Fig. 4b). Ten microliters of protein lysate was loaded per well. b Intron–exon structure of LDB3/ZASP. Exons 4a and 7 (shown in gray) are cardiac-specific and normally not present in skeletal muscle isoforms. Inclusion of these two exons was predicted to produce a protein of about 95 kD, as observed by western blot (Fig. 4a). Exons are not drawn to scale. c Representative RT-PCR assays to detect aberrant inclusion of exons 4a and 7. Arrows indicate the location of the primers for RT-PCR. Lanes are labeled 1 (DM1), 2 (DM2), N (normal), or L (100-bp ladder). Each predicted event is interrogated by two assays: one with primers flanking the aberrant exon, the other with the forward primer within the aberrantly spliced exon. The upper left panel shows the strong presence of cardiac exon 7 in DM but not in normal individuals. The presence of this exon is confirmed in the upper right panel. The lower left panel shows the presence of an isoform containing cardiac exon 4a in DM but not in normal individuals. This isoform is present more strongly in DM2 than DM1 patients. Exon 4a inclusion is confirmed in the lower right panel. The weak band (isoform containing 4a-4b-4c-5) represents a transcript which is not translated due to presence of a premature termination codon