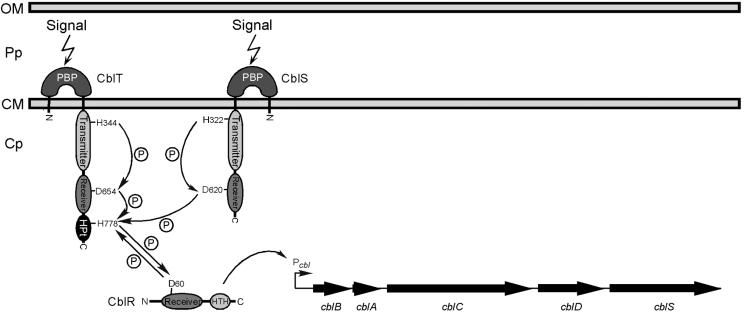
FIG. 8.
A working model for the CblSTR signal transduction pathway. (i) Upon receiving a signal from the environment via their periplasmic domains, the CblS and/or CblT hybrid sensor kinases undergo autophosphorylation at the histidine H322 or H344 residues, respectively, catalyzed by hydrolysis of ATP by the transmitter domain. It is also possible that CblS and CblT form homodimers and/or heterodimers, which may lead to cross-phosphorylation. (ii) Phosphotransfer reactions (indicated by arrows and circled P) are carried out between the transmitter, receiver, and HPt domains of CblS and CblT. The transfers of phosphoryl groups may occur intramolecularly and/or intermolecularly. (iii) The aspartate D60 in the receiver domain of the CblR response regulator is phosphorylated through interactions with the CblT HPt domain, leading to activation of CblR and transcription of the cblBACDS operon, possibly by directly binding the cblB promoter. Abbreviations: HPt, histidine phosphotransfer domain; HTH, helix-turn-helix domain; PBPb, bacterial periplasmic substrate-binding protein domain; Cp, cytoplasm; CM, cytoplasmic membrane; Pp, periplasm; OM, outer membrane.