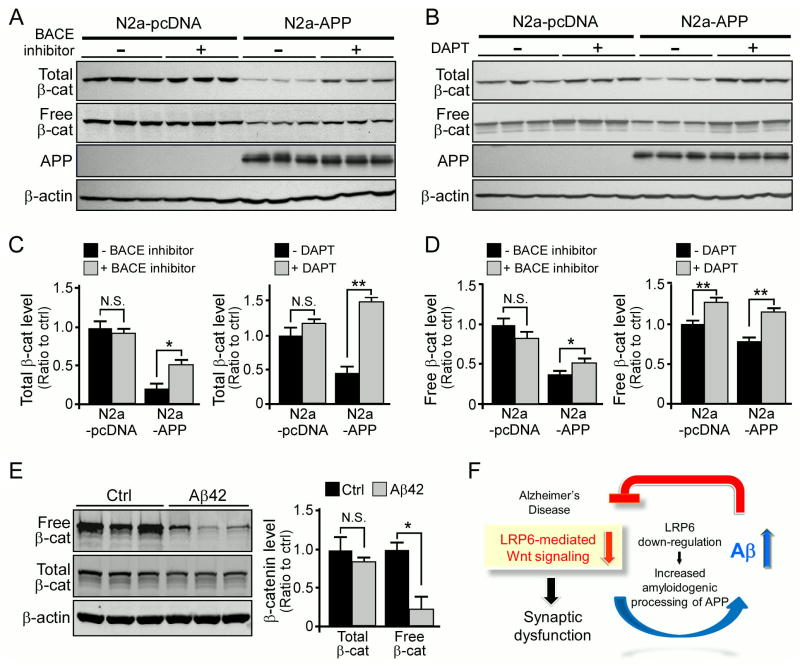
Figure 7. Aβ Suppresses LRP6 Expression and Wnt Signaling Activation.
(A–D) The levels of total β-catenin, free β-catenin, APP and β-actin in N2a-pcDNA and N2a-APP cells in the presence or absence of a BACE inhibitor (β-secretase inhibitor IV, 2μM) or a γ-secretase inhibitor (DAPT, 10 μM) examined by Western blot. Free β-catenin levels were analyzed by GST-E-Cadherin pull-down assay. Data represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; N.S., not significant.
(E) The levels of total and free β-catenin in primary neurons treated with 5 μM Aβ42 oligomers examined by Western blot. Data represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; N.S., not significant.
(F) Illustrative diagram depicting a potential vicious cycle between increased Aβ and decreased LRP6-mediated Wnt signaling in AD pathogenesis. See text for details.
See also Figure S7.