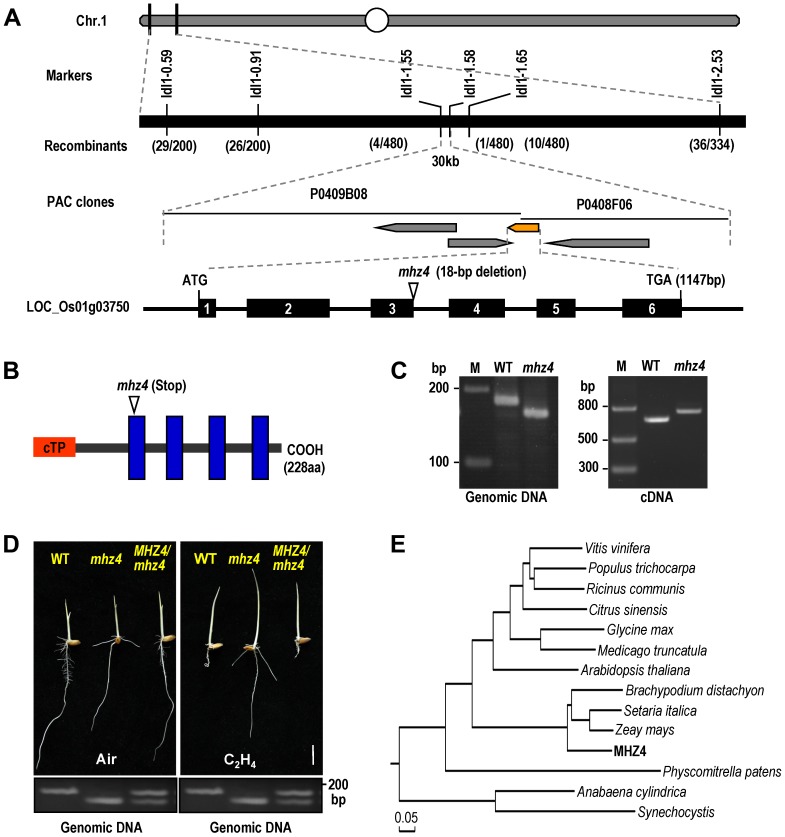
Figure 2. Map-based cloning of mhz4 locus.
(A) Fine mapping of MHZ4 gene. The locus was mapped to chromosome 1 within a 30 Kb region between Idl1–1.55 and Idl1–1.58 markers. Mutation site is indicated in schematic diagram of MHZ4 gene. Black boxes represent exons. (B) Schematic structure of the MHZ4 protein. The structure is predicted using the SMART software (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de). Mutation site is shown. cTP indicates chloroplast transit peptide identified using the ChloroP 1.1 program (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/ChloroP/). Blue columns represent transmembrane domains. (C) Confirmation of mhz4 mutation site in both genomic DNA and cDNA by PCR. M: marker. (D) Functional complementation of mhz4 mutant. MHZ4 genomic DNA (4213 bp) was transformed into mhz4 plants (MHZ4/mhz4), rescuing the enhanced coleoptile elongation and reduced root inhibition phenotypes of mhz4 in the presence of ethylene (10 ppm). Bottom is confirmation of the transgene by PCR using the genomic DNA as templates. Bar = 10 mm. (E) Phylogenetic analysis of MHZ4/OsABA4 and its homologous proteins from other plants. The phylogenetic tree is generated by Maximum Likelihood method. Accession numbers are as follows: Vitis vinifera, XP_002283875; Populus trichocarpa, XP_002305164; Ricinus communis, XP_002521222; Citrus sinensis, ADH82117; Glycine max, XP_003532342; Medicago truncatula, XP_003618901; Arabidopsis thaliana, NP_564889; Brachypodium distachyon, XP_003565288; Setaria italica, XP_004968073; Zeay mays, ACN29324; Physcomitrella patens, Pp1s108_75V6; Anabaena cylindrica, WP_015215835; Synechocystis, BAA18538.