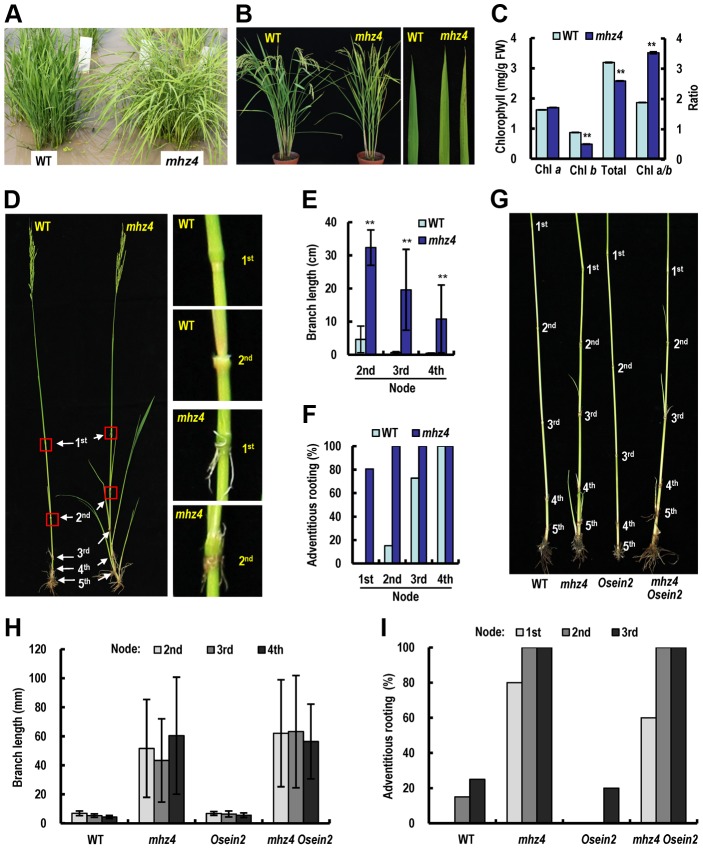
Figure 8. Phenotypic comparison of field-grown plants.
(A) Phenotypes of Five-week-old seedlings of WT and mhz4. (B) Plant phenotypes after heading. Please note the spots on some mhz4 leaves but not WT leaves. (C) Chlorophyll contents in the fourth leaves of plants. Chlorophyll was extracted with 95% ethanol from the fourth leaves from the top at heading stage. Each column is average of three measurements and bars indicate SD. ‘**’ indicate significant difference compared to WT (P<0.01). (D) Formation of branches and nodal adventitious roots in the main tiller of WT and mhz4 plants. (E) Branch length at each node from the main tillers of WT and mhz4. Each column is average of 30 to 35 plants and bars indicate SD. ‘**’ indicate significant difference compared to WT (P<0.01). (F) Percentage of nodal adventitious roots in the main tillers. 30 to 35 plants were investigated for WT and mhz4. (G) Effects of OsEIN2 mutation on branching and adventitious root formation of mhz4. Representative plants of WT, mhz4, Osein2 and mhz4 Osein2 double mutant were compared. (H) Quantification of branch length at each node in main tillers from 10–20 plants in (G). (I) Percentage of adventitious root formation at each node in main tillers from 10–20 plants in (G).