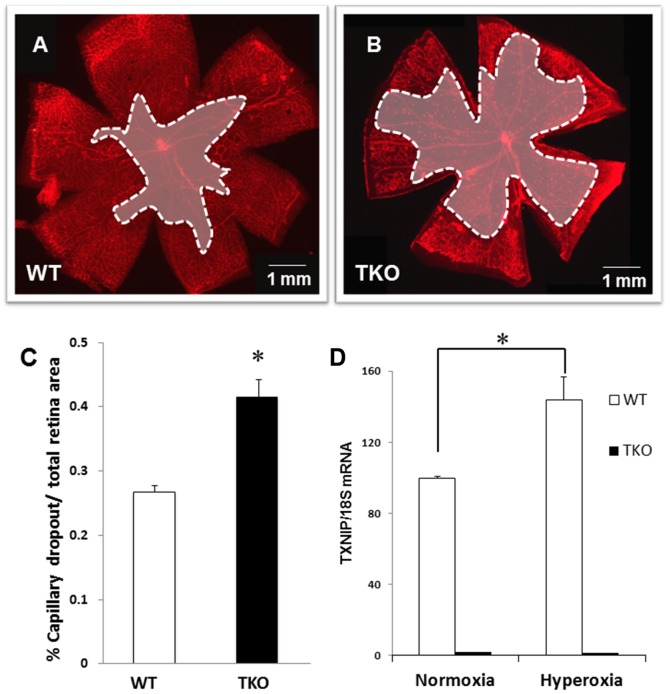
Figure 1. Deletion of TXNIP augments hyperoxia-induced vaso-obliteration compared to WT.
Wild type (WT) and TXNIP knockout (TKO) mice were subjected to hyperoxia (75% O2, p7–p12). Retinas were fixed and stained with iso-lectin B4 to quantify oxygen induced vaso-obliteration. A–C) Retinas from TKO mice exposed to hyperoxia showed significant increases in vaso-obliteration compared to WT. (*P<0.05 vs WT, n = 12). D) Hyperoxia stimulates TXNIP expression mRNA in WT but not in TKO mice. (*P<0.05 vs WT normoxia, n = 4)