Figure 8. Representative diagram shows the impact of TXNIP deletion on retina vasculature under both normoxia and hyperoxia.
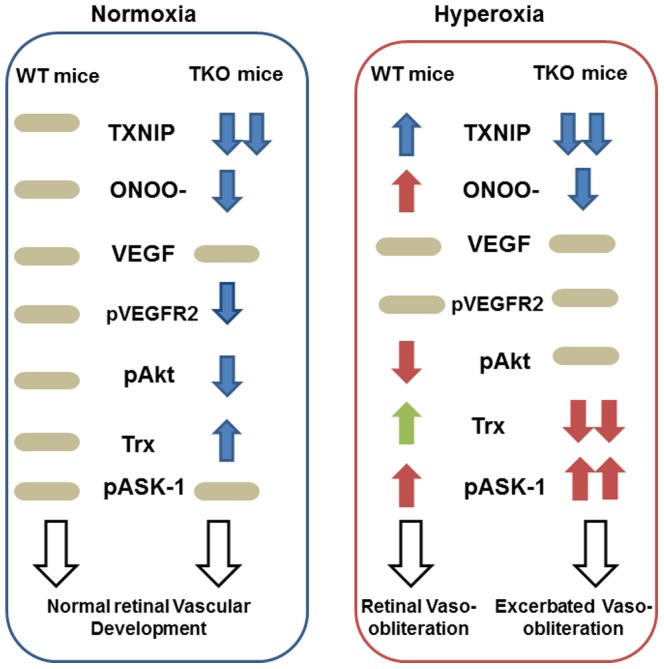
Under normoxia, retinas from TXNIP-deficient mice showed similar VEGF levels, less peroxynitrite (ONOO-) levels, less VEGF receptor-2 (pVEGFR2) activation and upregulated thioredoxin (Trx) that collectively lead to normal vascular development in comparison to WT mice. Under hyperoxia, retinas from WT mice showed higher peroxynitrite formation, less survival Akt activation (pAkt) and upregulated proapoptotic signal of ASK-1 resulting in vaso-obliteration. Retinas from TKO although showed less peroxynitrite levels and maintained Akt activation, retinas experienced significant decreases in thioredoxin (Trx) that shift the balance of the ASK-1-Trx inhibitory complex and increases the activation of the proapoptotic ASK-1 pathway leading to exacerbated vasoobliteration compared to WT.
