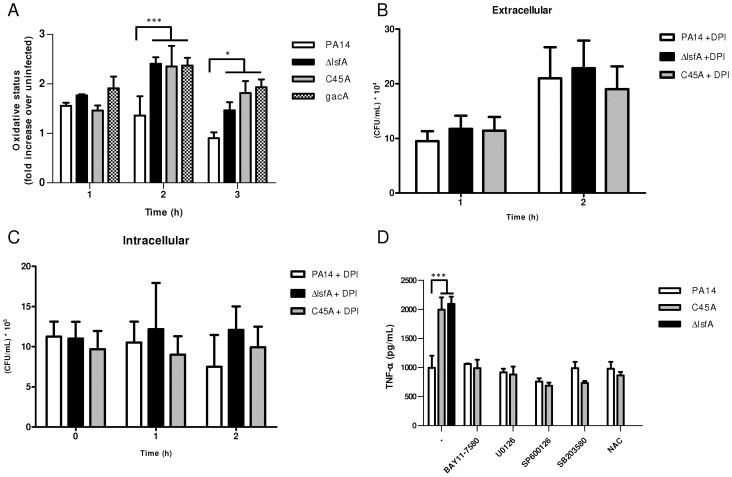
Figure 3. LsfA downregulates macrophages oxidative state that protected the bacteria against NADPH oxidase-generated ROS, and inhibits TNF-α production via the MAPK and NF-κB pathways.
(A) J774 cells were infected with PA14 or the ΔlsfA, C45A, or gacA mutants. After 1, 2 or 3 hours, the macrophages were washed with PBS and incubated for 15 min with H2DCFDA. Fluorescence was analyzed by FACS. (B) Macrophages were treated with DPI prior to infection. The supernatants were collected and diluted at the indicated time points, and the number of CFU was determined. (C) Cells were washed with PBS and R-10 containing 200 µg/mL gentamicin was added to the wells. At the indicated time points, the macrophages were lysed with Triton X-100. The released bacteria were diluted and number of CFU was determined (D) Macrophages were infected with PA14 or the lsfA mutants in the absence (-) or the presence of inhibitors of NF-κB (BAY11-7580), ERK (U0126), JNK (SP600125) and p38 (SB2035-80) or the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC). After 3 hours of infection, the supernatants were recovered, and TNF-α secretion was determined by ELISA. Data are the means ± SD from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *, p<0.05; ***, p<0.001.