Figure 6. IFN-γ and IL-1β induce DC-HIL expression by CD11b+Gr1+ cells.
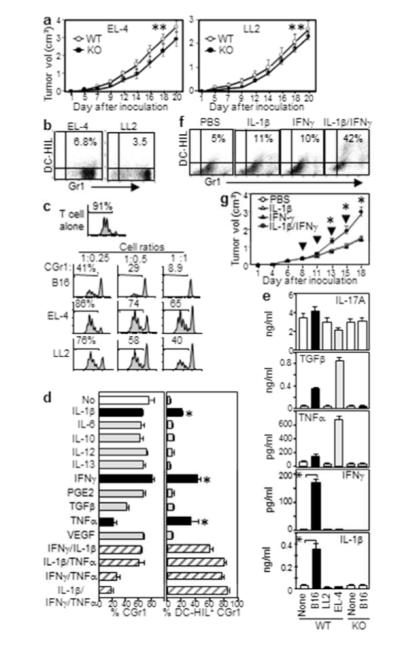
(a) Growth of EL-4 or LL2 tumor in WT or DC-HIL−/− mice (n=5, **p>0.05). CGr1 cells from those mice were examined for: Gr1 vs. DC-HIL expression (b) and suppression of CFSE-labeled T-cells activated by anti-CD3/CD28 (c). (d) Linneg BM cells cultured with cytokines were assayed for % CGr1 or DC-HIL+ cells among CD11c+/CD19+-depleted or total CGr1 cells, respectively (mean ± sd, n=3). (e) Blood from WT or DC-HIL KO mice (n=5) with or without (None) tumor measured for cytokines. (f) DC-HIL vs. Gr1 expression by CGr1 cells within LL2 tumor on mice one day after the second intratumoral injection of cytokines. (g) Tumor volume after cytokines injected intratumorally (arrows) into LL2 tumor-bearing mice. *p<0.01.
