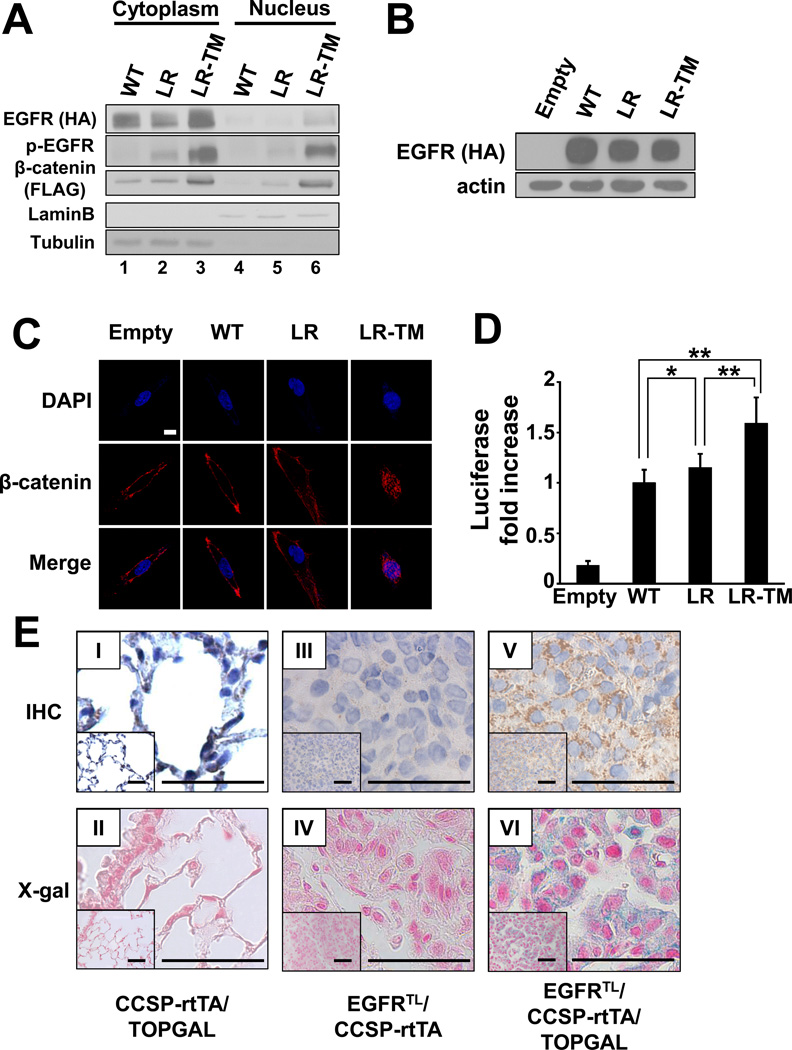
Figure 2. β-catenin is stabilized and activated by EGFR mutants.
(A) Immunoblots of fractionated extracts from 293T cells co-transfected with constructs containing FLAG-tagged β-catenin and either HA-tagged wild type EGFR (WT), EGFR-L858R (LR), or EGFR-L858R-T790M (LR-TM). (B) Immunoblots of whole extracts from BEAS-2B cells stably expressing HA-tagged wild type EGFR (WT), EGFR-L858R (LR), or EGFR-L858R-T790M (LR-TM). BEAS-2B cells infected with MigR1 empty vector were used as a control. (C) Confocal images of stable BEAS-2B cells described in (B). Cells were incubated with anti- β-catenin antibody and visualized by Alexa Fluor 488. Scale bar = 10 µm. (D) Transactivation of β-catenin measured by luciferase activity. Data represents mean ± standard deviation from eight independent experiments. * indicates p ≤ 0.05. ** indicates p ≤ 0.01. (E) Immunohistochemical analysis of β-galactosidase (I, III, V) and X-gal staining (II, IV, VI). Lungs isolated from CCSP-rtTA/TOPGAL (I, II), EGFRTL/CCSP-rtTA (III, IV), and EGFRTL/CCSP-rtTA/TOPGAL (V, VI) are shown. Scale bar = 50 µm.