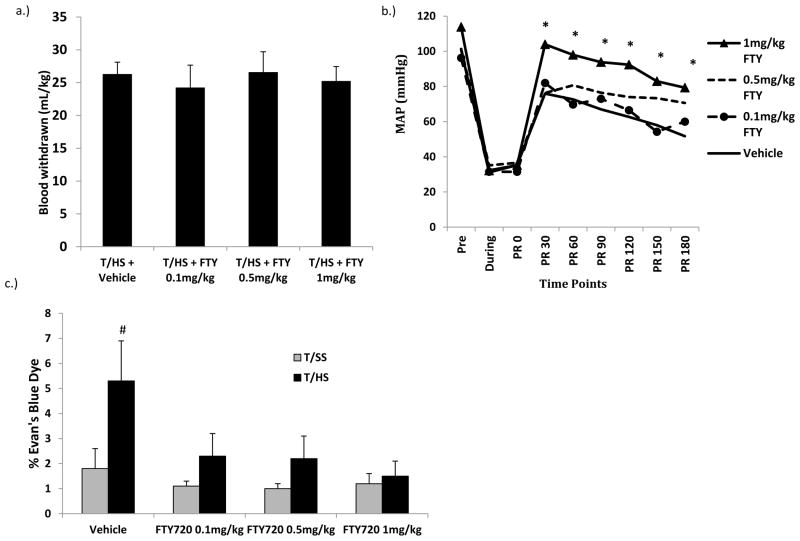
Figure 1.
A) There were no differences in the volume of blood required to be withdrawn to induce and maintain shock. B) The average MAP post resuscitation was significantly higher in the 1mg/kg FTY720 dose group compared with the vehicle group. All FTY720 doses were effective in limiting T/HS-induced C) lung injury
Data expressed as Mean ± SD except for Figure 1b, where the mean value without SD was used for clarity. n=6–9 rats per group; # p<0.05 vs. all other groups; * p<0.05 vs. THS + Vehicle; PR=Post Resuscitation.