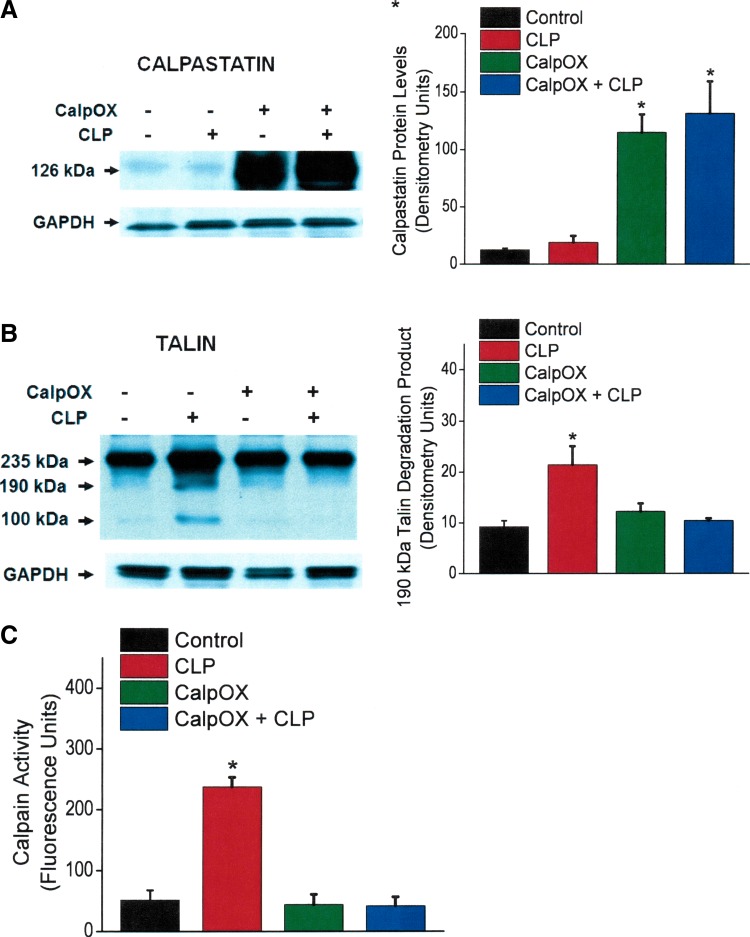
Fig. 3.
Diaphragm calpastatin protein levels (A), talin protein levels (B), and diaphragm calpain activity (C) for the four experimental groups. Bars indicate controls (black), CLP animals (red), CalpOX animals (green), and CalpOX + CLP animals (blue). Left: representative Western blots. Right: group mean densitometry levels for protein bands. GAPDH was used a loading control. Calpastatin levels for the CalpOX animals were 10- to 15-fold higher than levels in WT animals (A). CLP-induced sepsis did not significantly alter calpastatin levels in WT or calpastatin-overexpressing animals. B: CLP increased talin degradation in WT animals (P < 0.006). Calpastatin-overexpressing animals were resistant to diaphragm talin cleavage, with talin degradation protein levels for calpastatin-overexpressing CLP animals similar to levels for WT sham-operated animals. C: we found that CLP induced a large increase in diaphragm calpain activity in WT mice (P < 0.001). Calpastatin overexpression prevented CLP-induced calpain activation, with calpain activity levels for sham-operated and CLP calpastatin-overexpressing mice similar to sham-operated WT controls. *Statistical significance.