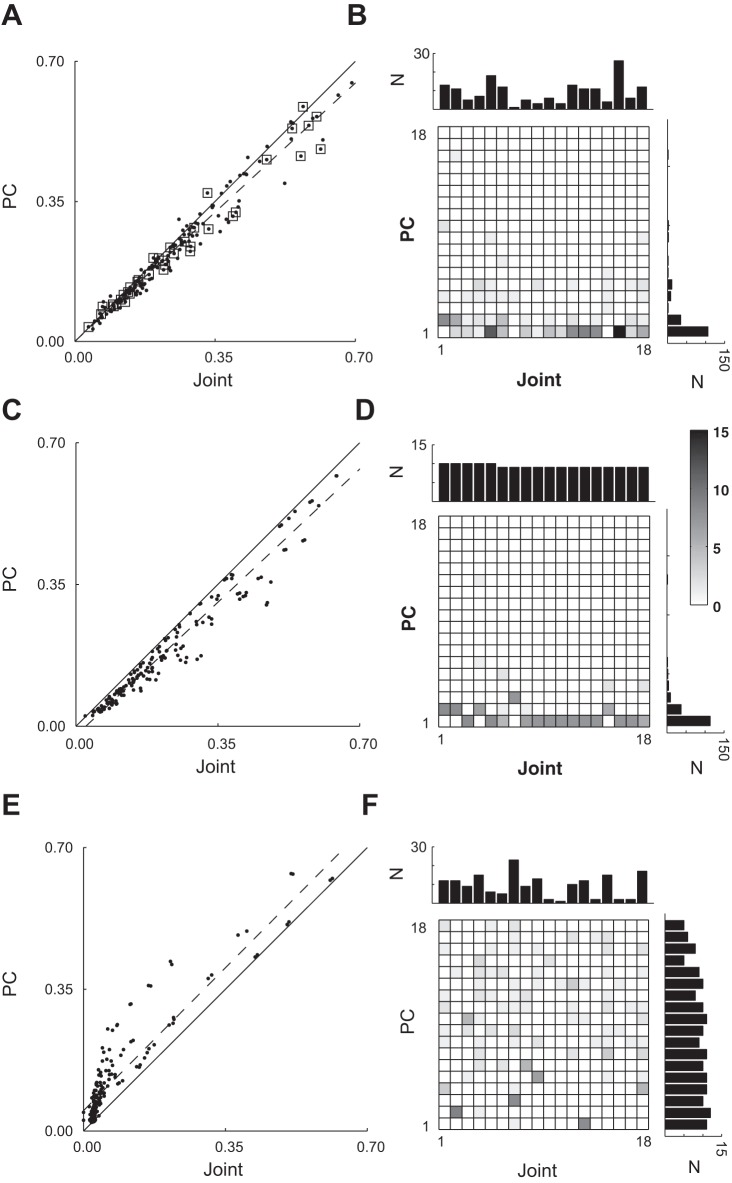
Fig. 7.
Maximal absolute cross-correlations with joint DoFs vs. PCs. A: in this scatterplot, each point represents a spike recording plotted at the coordinates of its maximum significant absolute cross-correlation (MAXC) with any joint (abscissa) vs. its MAXC with any PC (ordinate). Points representing single units (SUs) have been marked with open squares; other points represent multiunit (MU) recordings. The solid line has a slope of 1.0, and the dashed line is the linear regression best fit to the data (SUs + MUs). B: two-dimensional histogram and marginal one-dimensional histograms show the number of spike recordings that had their MAXC with each joint DoF and with each PC. The data shown in A and B represent all spike recordings (SUs + MUs) from session X0918. C and D represent identical analysis performed after replacing each real spike recording with a simulated recording created to correlate with a joint angle from session X0918, whereas E and F represent identical analysis performed after replacing each real spike recording with a simulated recording created to correlate with one of the PCs.