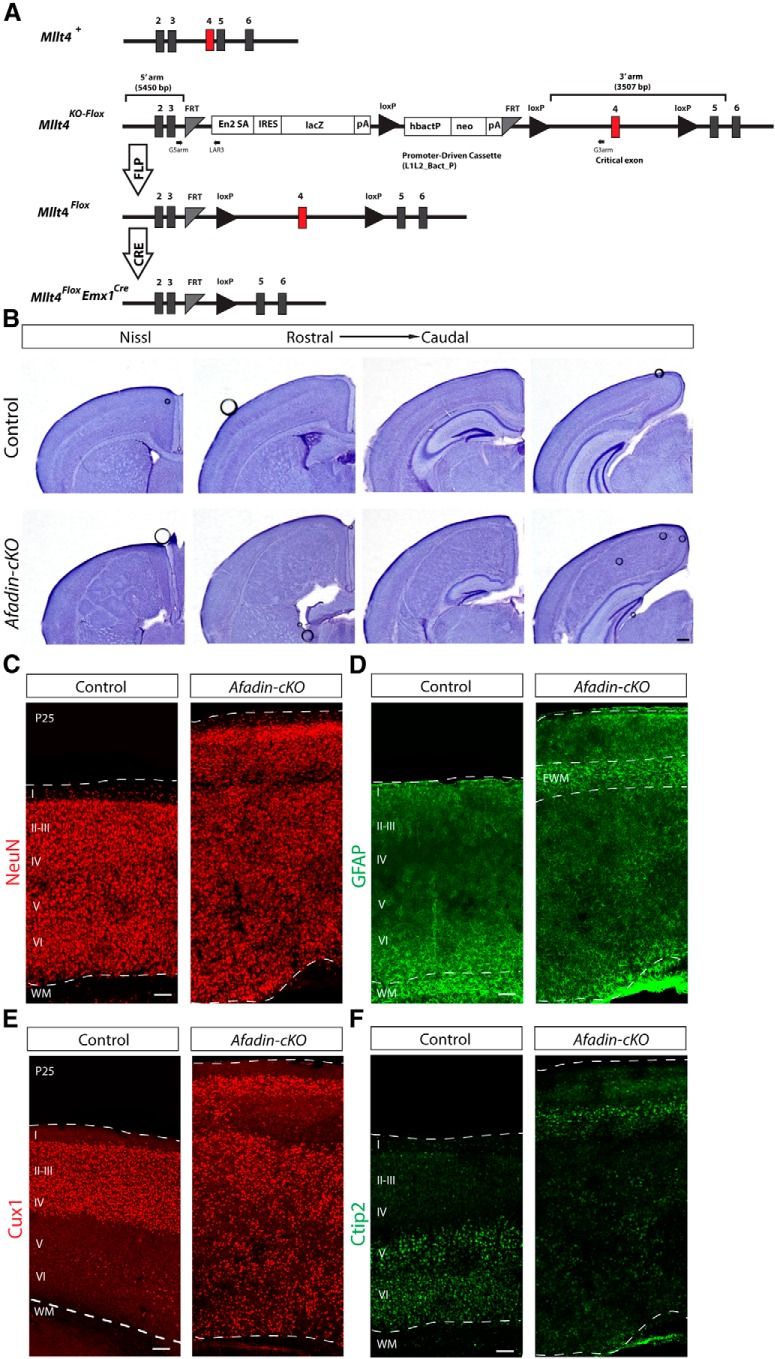
Figure 1.
Afadin deletion from cortical progenitors causes SBH or double cortex. A, Afadin-cKO generation. Schematic diagram of wild-type (+), knock-out first mutation with conditional potential (KO-flox), floxed (flox), and Cre-recombined alleles of the Mllt4 gene. The EUCOMM “knock-out first” allele (KO-flox) contains an IRES:lacZ trapping cassette and a floxed promoter-driven neo cassette inserted into an intron of the targeted gene. Engrailed (En2) splice acceptor disrupts gene function, resulting in a lacZ fusion for studying gene expression. Flp recombinase removes the gene trap cassette, converts the “knock-out first” allele to a conditional allele (flox). Cre recombinase deletes the floxed exon of the conditional allele resulting in a frame shift and null mutation (modified from Ryder et al., 2013). Numbered boxes represent exons. Red box represents the critical exon. PCR primers for genotyping (G5arm, G3arm, and LAR3) are indicated. B, Nissl staining showing coronal sections of adult brains from control and Afadin-cKO mice at several histological levels along the rostrocaudal axis of the neocortex. Note the enlarged neocortex and the ectopic mass of cells surrounded by cell-sparse regions in the mutant mice. Scale bar, 500 μm. C, D, Coronal sections of adult brains from control and Afadin-cKO mice immunostained with the neuronal marker NeuN (red; C) and with the astrocyte marker GFAP (green; D). Note the ectopic accumulation of GFAP+ astrocytes, presumably ectopic white matter, in the upper part of the cortex of the mutant mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. E, F, Coronal sections of adult brains from control and Afadin-cKO mice immunostained with the upper layer marker Cux1 (red; E) and the lower layer marker Ctip2 (green; F). Note the abnormal distribution of the cells in the Afadin-cKO mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. I-VI, layers I–VI; WM, white matter; EWM, ectopic white matter.