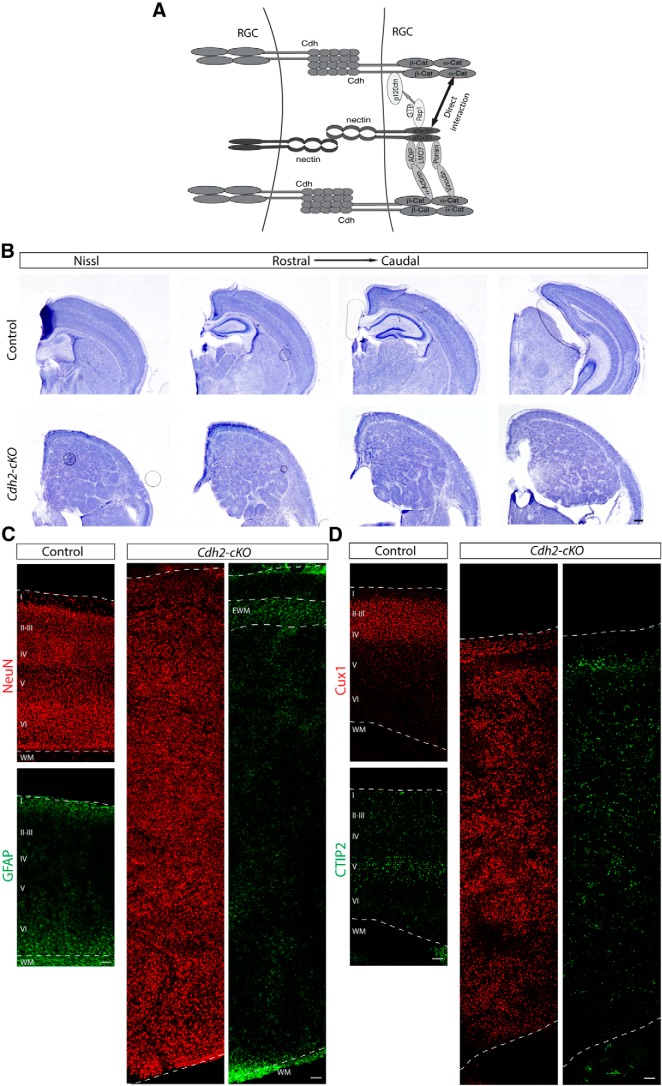
Figure 6.
Cdh2 deletion in the cortical progenitors causes severe cortical lamination defects. A, Diagram showing the different interactions described for afadin and cadherins in adherens junction formation. B, Nissl staining showing coronal sections at several histological levels along the rostrocaudal axis of the neocortex of P13 brains of control and Cdh2-cKO the mice. Note hyperplastic and disorganized cortex and the presence of a cell-sparse region in the upper part of the cortex on top of a hyperplastic ectopia in Cdh2-cKO mice. Scale bar, 500 μm. C, Coronal sections of adult brains from control and Cdh2-cKO mice immunostained for the neuronal marker NeuN (red) and the astrocyte marker GFAP (green). Note the presence of GFAP+ cells, presumably ectopic white matter, in the upper part of the cortex of Cdh2-cKO mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. D, Coronal sections of adult brains from control and Cdh2-cKO mice immunostained for Cux1 (red) and Ctip2 (green). Note the abnormal distribution of neuronal subtypes in Cdh2-cKO mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. Abbreviations as in Figure 1.