Figure 2.
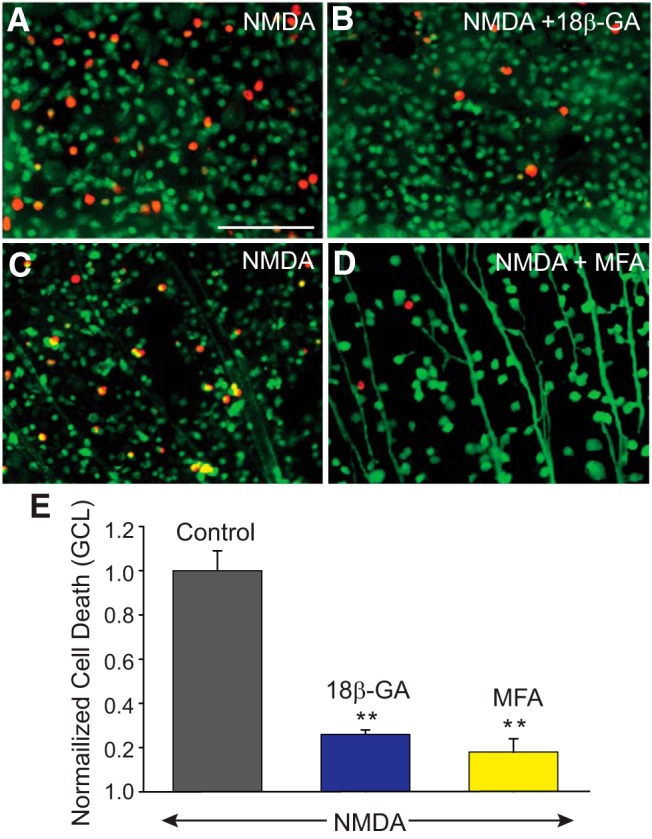
NMDA-induced excitotoxic cell death is significantly reduced by GJ blockers. A, C, NMDA-induced cell death in the GCL of control retinas, and those treated for 30 min with 25 μm of 18β-GA (B), or 50 μm of MFA (D) before exposing to NMDA (300 μm). Top, Experiments in which live and dead cells are marked with calcein-AM (green) and ethidium homodimer (EthD, red), respectively. Bottom, Experiments in which retrograde labeling through optic nerve cut with LY was used to label RGCs and then retinas processed with EthD to detect dead cells. E, Histogram represents the protective effect of GJ blockers on RGCs against NMDA-induced excitotoxicity. The number of dead cells was counted manually per unit area from 5 different visual fields in the GCL of whole-mount retinas pretreated with 18β-GA (n = 12/n = 3), or MFA (n = 42/n = 5), and numbers were normalized to one obtained in retinas exposed to NMDA alone (control, n = 44/n = 5). **p < 0.001 versus control. Scale bar, 100 μm.
