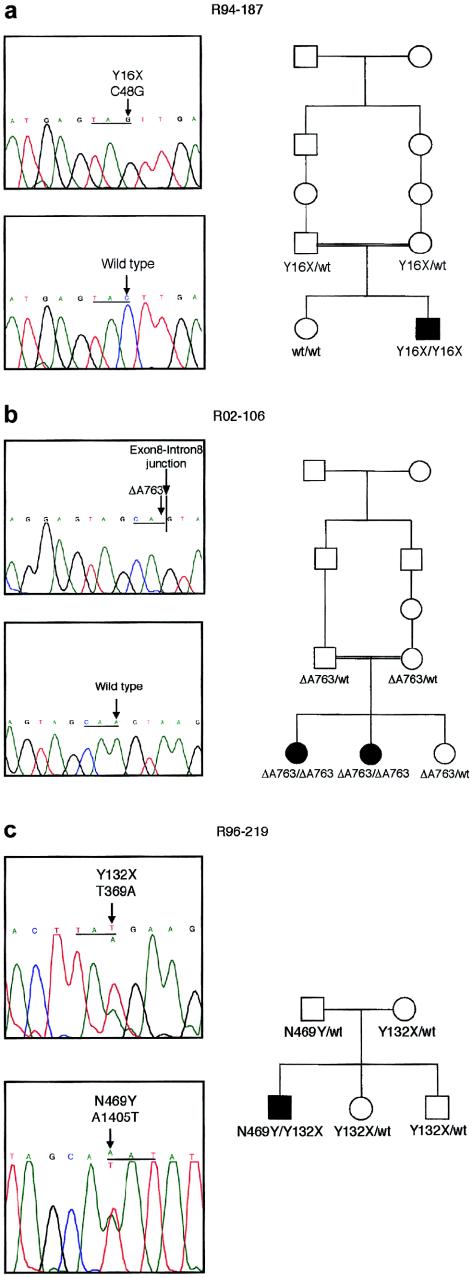
Figure 2.
Mutations in DMC. a, Chromatograms showing the mutation in family R94-187 and (below) a normal sequence. The sequence, with the mutant nucleotide and the corresponding normal nucleotide identified with an arrow, is shown above, and the reading frame is underlined. The nucleotide sequence is numbered from the beginning of the coding sequence. The pedigree, demonstrating segregation of the mutation in the family, is shown to the right. b, Chromatograms showing the mutation in family R02-106, together with a normal sequence. An arrow identifies the mutant nucleotide and the corresponding normal nucleotide, and the reading frame is underlined. A vertical line identifies the exon-intron junction. Segregation of the mutation in the family is shown on the pedigree to the right. c, Chromatograms showing the two mutations identified in family R96-219. The reading frame is underlined, and, in each panel, an arrow identifies the normal (above) and mutant (below) sequences. Segregation of the mutations in the family is shown on the pedigree to the right.