Figure 2.
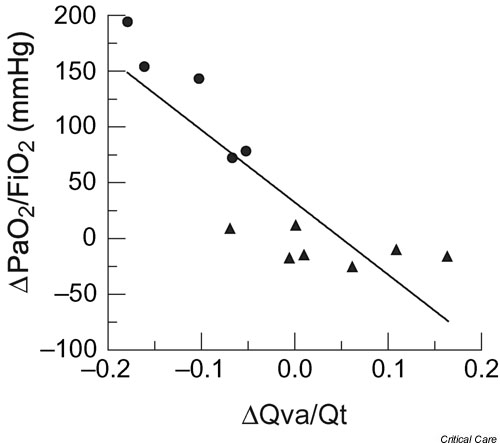
Relationship between recruitment maneuver (RM)-induced changes in arterial oxygen tension (PaO2)/fractional inspired oxygen (FiO2) and RM-induced changes in pulmonary shunt (Qva/Qt). A significant negative correlation was found between these two parameters (r = -0.85; P < 0.01). In these patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), who were near optimally recruited by positive end-expiratory pressure and tidal volume, the addition of a RM induced alveolar overdistension with redistribution of blood flow and consequently an increase in intrapulmonary shunt. Responders: solid circles; nonresponders: solid triangles. Reproduced and modified with permission from reference Villagrá and coworkers [33].
