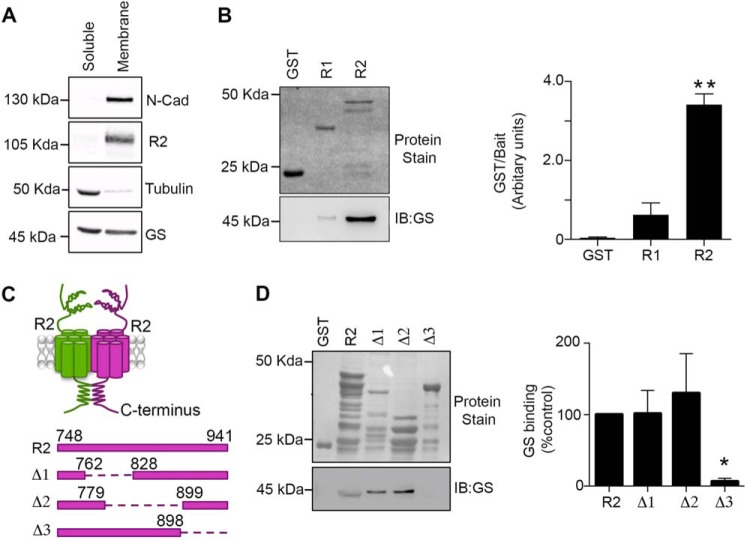
FIGURE 1.
GS binds to the cytoplasmic tail of GABABR2. A, soluble and membrane fractions prepared from hippocampus were immunoblotted with N-cadherin (N-cadh), R2, tubulin, and GS antibodies. B, fusion proteins were exposed to hipppocampal extracts, subject to SDS-PAGE, transferred to a membrane stained with Ponceau S (upper panel) or immunoblotted with GS antibody (lower panel). GS levels were then compared with those seen with GST. Data represent mean ± S.E. (p < 0.01; ANOVA, n = 3). C, a schematic of the GST-R2 deletion constructs used for experimentation. D, fusion proteins were exposed to hippocampal extracts and processed as detailed above. The levels of GS binding were normalized to values for GST-R2. Data represent mean ± S.E. (p < 0.05; ANOVA, n = 4). *, significantly different from control, (p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01).