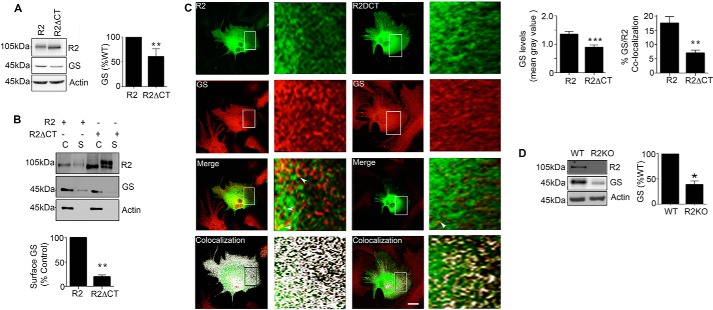
FIGURE 7.
GABABRs regulate GS expression levels in cultured astrocytes and the brain. A, astrocytes expressing R2 or R2ΔCT were immunoblotted with R2, GS, and actin antibodies. The ratios of GS:R2 and GS:R2ΔCT immunoreactivity were determined and normalized to values for GS:R2. Data represent mean ± S.E., p < 0.01; unpaired t test, n = 5. B, astrocytes transfected with R2, or R2ΔCT were labeled with NHS-Biotin. After purification on avidin the resulting cytosolic (C) and surface (S) fractions were immunoblotted with R2, GS, and actin antibodies. GS levels in surface fractions were normalized to levels seen for cells expressing R2. Data represent mean ± S.E., (p < 0.01; unpaired t test, n = 4). C, astrocytes transfected with R2 or R2ΔCT and stained with Flag (green) and GS (red) antibodies followed by confocal microscopy; scale bar, 20 microns. Arrows indicate co-localized puncta of GS/R2 immunoreactivity, and in the lower panel co-localization as determined using ImageJ is shown in white. The level of endogenous GS in R2-positive puncta was then determined and expressed as mean gray value (p < 0.001; unpaired t test, n = 4). In the lower panel, co-localization between GS and R2, or GS and R2ΔCT were determined. Data represent mean ± S.E., p < 0.01; unpaired t test, n = 3. D, detergent solubilized hippocampal extracts were from WT and R2KO mice were immunoblotted with R2, GS, and actin antibodies. The levels of GS were determined and normalized to values in WT mice (p < 0.05; unpaired t test, n = 6). *, significantly different from control, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.