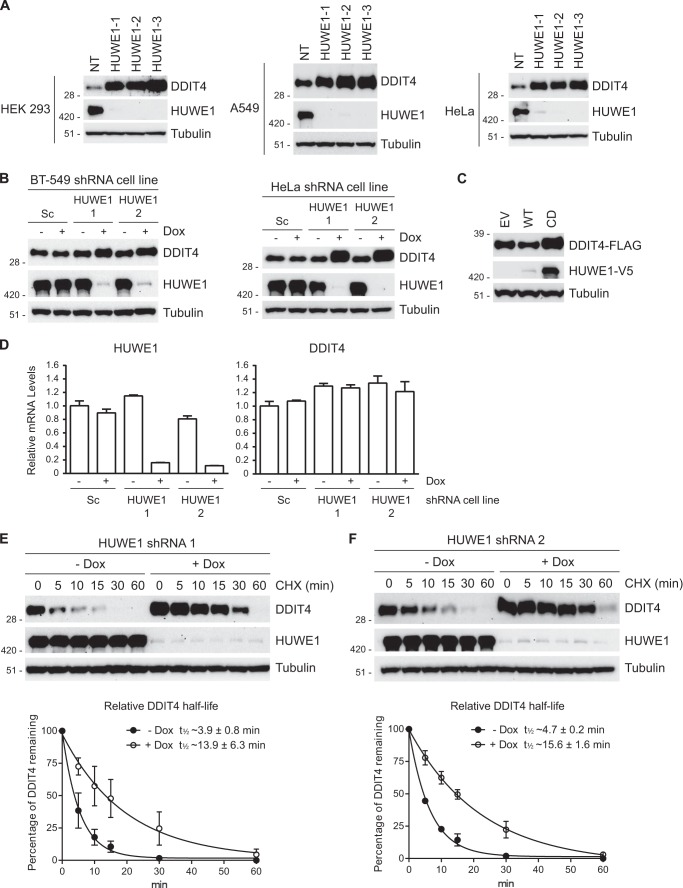
FIGURE 4.
HUWE1 regulates the accumulation and stability of DDIT4. A, several human cells lines were transfected with non-targeting (NT) control or three HUWE1 siRNAs for 72 h and analyzed by immunoblotting. B, HeLa and BT-549 cells stably expressing Dox-inducible scrambled (Sc) or two unique HUWE1 shRNAs were treated in the absence or presence of Dox for 72 h. Immunoblotting demonstrates that silencing of HUWE1 increases steady-state levels of DDIT4. C, HEK 293T cells were co-transfected with plasmids expressing DDIT4-FLAG and either empty vector (EV), WT, or CD HUWE1-V5 proteins for 24 h. DDIT4-FLAG levels were assessed by immunoblot analysis. D, HeLa cells stably expressing Dox-inducible scrambled (Sc) or two unique HUWE1 shRNAs were treated in the absence or presence of Dox for 72 h. Relative HUWE1 and DDIT4 mRNA levels were measured by quantitative PCR. Assays were performed in triplicate with data represented as the means ± S.E. E and F, HeLa cells stably expressing a Dox-inducible HUWE1 shRNA were treated in the absence or presence of Dox for 72 h. Cells were incubated with cycloheximide (CHX) and harvested at the indicated time points. Top panels, DDIT4 levels as measured by immunoblotting. Bottom panels, half-life of DDIT4 based on the quantitation of three independent immunoblots. Error bars represent S.E.