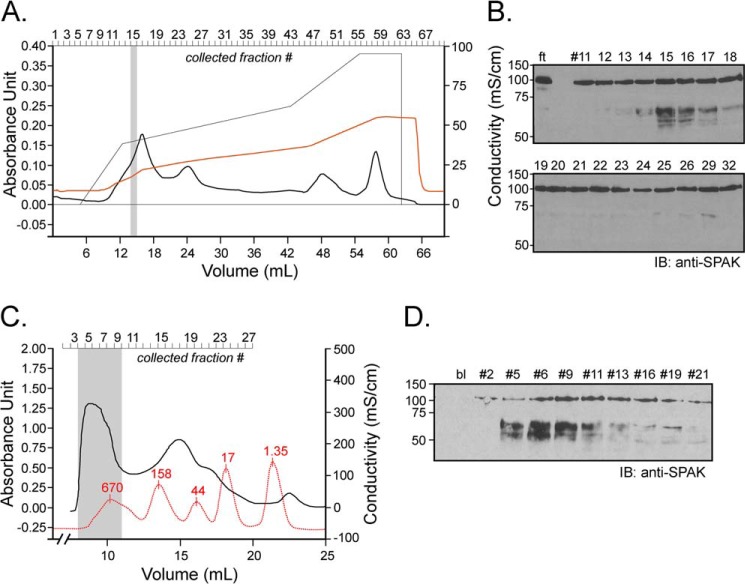
FIGURE 5.
Ion exchange and size exclusion chromatography. A, 1 ml of kidney lysate (25 μg/μl) was diluted on ice into 10 mm Tris/HCl, pH 8.5, and loaded onto a 5-ml Q-column. After washing the column with this buffer, a salt gradient (50 mm to 500 mm NaCl) was applied (see the thin black line). Absorbance at 280 nm and conductivity were followed over time (thick black line and red line, respectively). B, equal fraction volumes (20 μl) were diluted in phosphate buffer and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C with 2 μl of SPAK fusion protein (5 μg/μl). ft is the flow-through, proteins that are not bound to the cation exchange column. IB, immunoblot. C, kidney lysate was dialyzed through a 14-kDa dialysis membrane for 2 days. After recovery, 1 ml of dialyzed sample was subjected to Superdex 200 gel filtration, and 0.5-ml fractions were collected. After the run of the sample, an identical run was performed with Bio-Rad standards (red curve). Note that for clarity of the figure, the standard curve was reduced vertically to 40% of its original size. Proteins in standard were thyroglobulin (670 kDa), γ-globulin (158 kDa), ovalbumin (44 kDa), myoglobulin (17 kDa), and vitamin B (1.35 kDa). D, equal amounts of protein (9 μg) from each fraction was diluted in phosphate buffer and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C with 2 μl of SPAK fusion protein (40 μl total reaction volume). Samples were subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis using 1:1000 anti-SPAK C-terminal antibody followed by 1:5000 HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody.