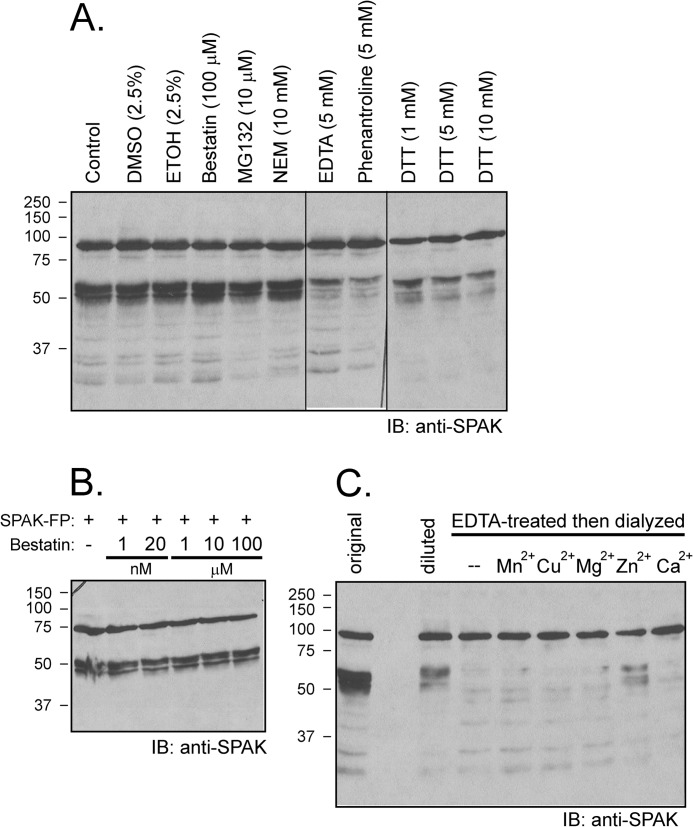
FIGURE 6.
Cleavage is prevented by excess EDTA and by 1,10-phenanthroline and DTT but not by bestatin. A, samples containing 70 μg of kidney lysate were preincubated for 30 min at 37 °C in phosphate buffer with different inhibitors (final concentration: 100 μm bestatin, 10 μm MG132, 10 mm N-ethylmaleimide (NEM), 5 mm EDTA, 5 mm 1, 10-phenanthroline, 1 mm DTT, 5 mm DTT, 10 mm DTT) or with vehicle before reactions for 1 h at 37 °C with 2 μl of SPAK fusion protein (5 μg/μl). IB, immunoblot. B, absence of bestatin effect at concentrations ranging from 1 nm to 100 μm. Western blot analysis was done using 1:1000 anti-SPAK (C-terminal) antibody followed by 1:5000 HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody. FP, fusion protein. C, the protease that cleaves SPAK is a Zn2+ metalloprotease. Kidney lysate was incubated with 20 mm EDTA for 1 h at 37 °C followed by 2 days of dialysis at 4 °C to wash away the EDTA. Recovered lysate was then concentrated using a 30-kDa centrifugal filter (Millipore) and preincubated (4 μg) with or without 1 mm concentrations of different divalent cations for 30 min before reaction with GST-SPAK fusion protein for 1 h at 37 °C. Reaction between non-EDTA-treated kidney lysate (4 μg, diluted) and SPAK fusion protein was used as positive control. Typical reactions between 1 μl of kidney lysate (22 μg/μl, original) and 2 μl of SPAK fusion protein was also used as a positive control. Samples were subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE followed by Western blot analysis as described before.