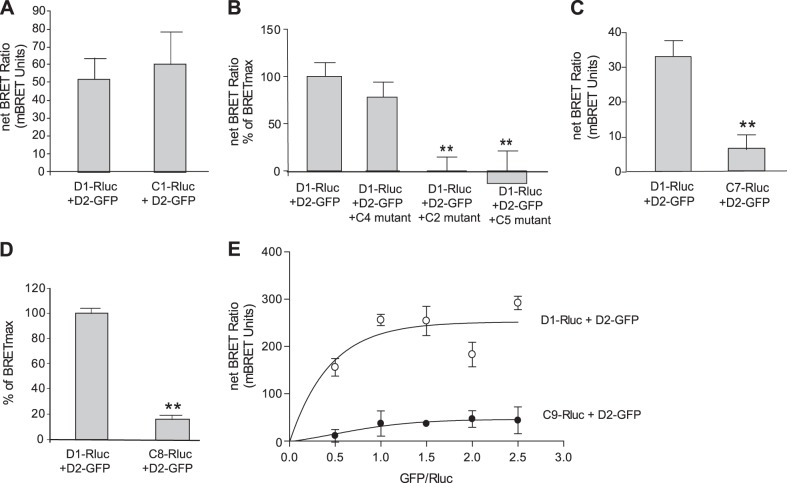
Figure 3.
Defining the amino acids from the D1 C tail involved in D1-D2 heteromer formation. Serial mutations and deletions were performed to define the amino acids from D1 C tail involved in the D1-D2 interaction (Table 1). A) BRET analysis between D2-GFP and either D1-Rluc or C1-Rluc. B) Effects of coexpressing mutants C2, C4, or C5 on D1-D2 heteromer interaction. A BRET signal was obtained between D1-Rluc and D2-GFP, which was abolished by coexpressing C2 or C5 deletion mutants but not by coexpression of C4 deletion mutant, indicating the involvement of the amino acids deleted in C4. C) Comparison of BRET signal generated from the interaction of D2-GFP with either D1-Rluc or the C7-Rluc mutant, in which 6 aa (402Lys–Ala407) were deleted. D) The 4 aa (402Lys–Glu405) were substituted by alanines in the C8 mutant. Graph shows a comparison of BRET signal between D2-GFP and either D1-Rluc or C8-Rluc. E) BRET saturation-curve analysis of D2-GFP and either D1-Rluc or C9-Rluc. C9 mutant has 2 glutamic acids (404E and 405E) substituted by alanines. Results represent means ± sem from 3 independent experiments (n=3). **P < 0.01.