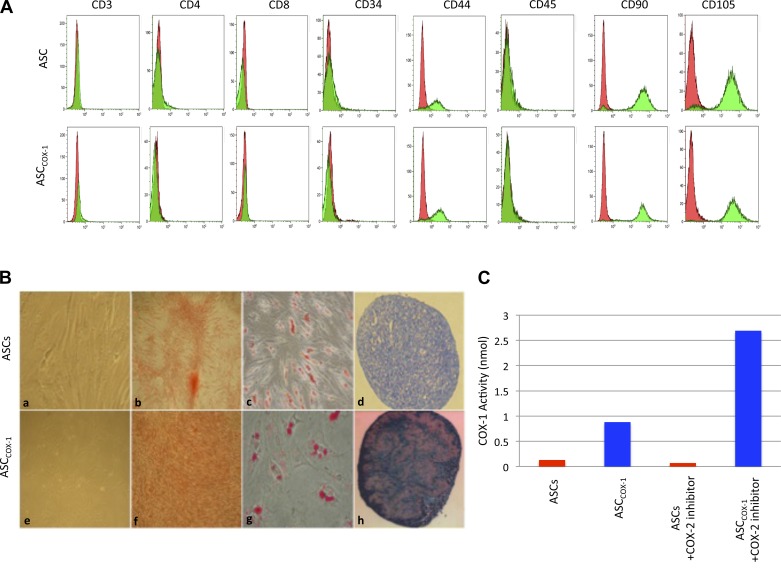
Fig. 2.
Adipose stem cells (ASCs) and ASCCOX-1 cell characteristics. A: immunophenotypic analyses of cell surface profile was determined by flow cytomety. Cultured ASCs and ASCCOX-1 were stained with monoclonal antibodies for CD105, CD90, CD44, CD34, CD45, CD4, and CD11b. Flow cytometry histographs are representative of triplicate experiments from each clone. B: ASCCOX-1 maintained their stem cell characteristics identical to ASCs and displayed mesenchymal markers (a and e). The ASCs and ASCCOX-1 cells were capable of differentiating into osteogenic (b and f; differentiated cells were stained with alizarin red), adipogenic (c and g; differentiated cells were stained positive for intracellular lipid vesicles using Oil Red O), and chondrogenic (d and h; extracellular proteoglycans were stained with toluidin blue). C: COX-1 enzyme activity was evaluated using the Cayman COX-1 activity assay. The cell lysates of ASCs and ASCCOX-1 were assayed for COX-1 activity measured using the ELISA kit.