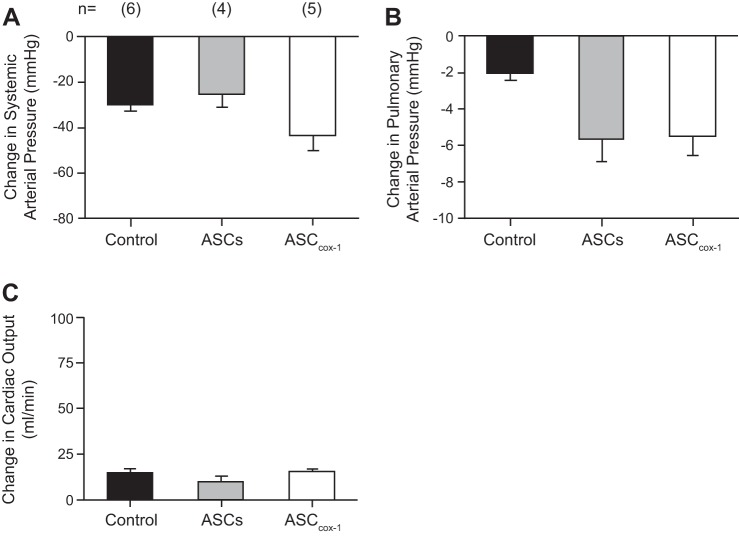
Fig. 4.
Bar graphs comparing the change in systemic arterial pressure (A), pulmonary arterial pressure (B), and cardiac output (C) in response to an intravenous injection of sodium nitroprusside (SNP; 3 μg/kg) in control rats, MCT rats treated with untransduced ASCs, and MCT-treated rats treated with ASCCOX-1 cells. The decrease in pulmonary arterial pressure in response to iv injection of SNP was significantly greater in animals treated with MCT plus ASCs and MCT plus ASCCOX-1 compared with the healthy control, P < 0.05 ANOVA and Dunnett's test; n = number of animals. (The decrease in pulmonary arterial pressure in MCT-treated animals was not different from the decrease in pulmonary arterial pressure in response to SNP when pulmonary arterial pressure was increased using U46619; Ref. 18.) These results indicate that decreases in pulmonary artery pressure in response to iv injection of SNP were similar in ASC-treated and ASCCOX-1-treated rats that had been injected with MCT compared with rats in which the pulmonary artery pressure was increased with U46619. The decreases in pulmonary arterial pressure in response to SNP were significantly smaller in healthy control animals that were not treated with MCT and have very little vasoconstrictor tone in pulmonary vascular bed.