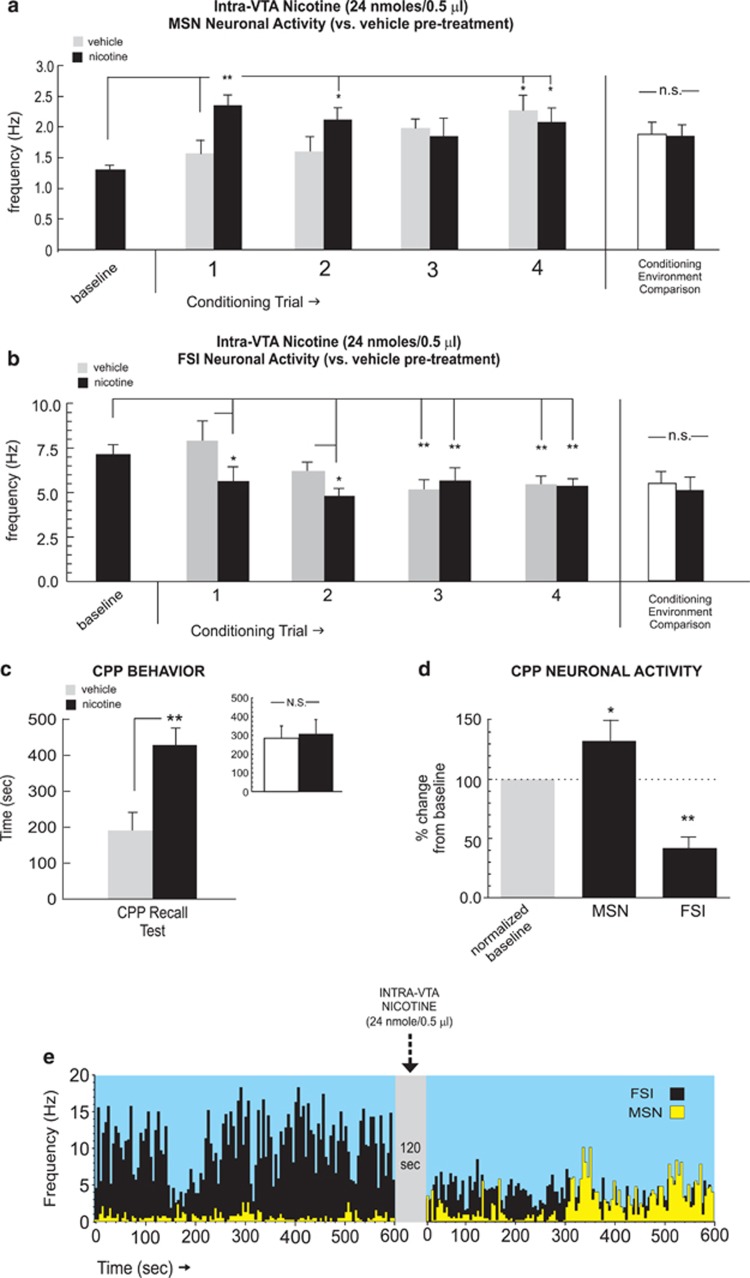
Figure 3.
NAshell neuronal group activity patterns during intra-ventral tegmental area (VTA) nicotine reward learning. (a) Neuronal activity patterns during vehicle or nicotine (24 nmol/0.5 μl) conditioning sessions for isolated medium spiny neurons (MSNs). Total average MSN neuronal activity patterns did not differ across the different conditioning environments, independently of drug treatment (far right side). (b) Neuronal activity patterns during vehicle or nicotine fast-spiking interneuron (FSI) neuronal units. Total average FSI neuronal activity patterns did not differ across the different conditioning environments, independently of drug treatment (far right side). (c) Rewarding behavioral effects of intra-VTA nicotine demonstrated by conditioned place preference (CPP) for nicotine-paired environments during testing. Inset shows average times spent in the separate conditioning environments, independently of treatment condition. (d) Relative to baseline activity, MSNs displayed increased activity and FSIs demonstrated inhibited activity during the CPP test. (e) Representative MSN/FSI rastergram overlay, showing 10 min pre intra-VTA nicotine (24 nmol/0.5 μl) vs post-activity levels with characteristic increased spontaneous firing. In contrast, FSIs typically displayed increased activity following intra-VTA nicotine infusions. Bars represent mean±SEM for this and subsequent figures. *p<0.05; **p<0.01. NAshell, shell region of the NAc; N.S., not significant.