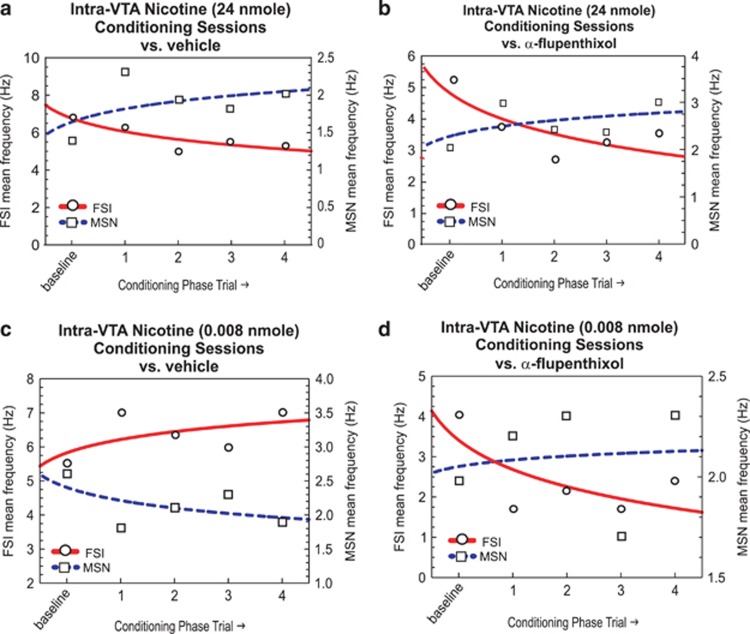
Figure 9.
Summary of NAshell fast-spiking interneuron (FSI) vs medium spiny neuron (MSN) activity patterns during nicotine conditioning sessions. (a) Acutely rewarding intra-ventral tegmental area (VTA) nicotine (24 nmol/0.5 μl) evokes increased MSN and decreased FSI activity over conditioning trials, while (b) challenge of this dose of intra-VTA nicotine with α-flupenthixol (α-flu) pre-treatment does not alter this activity pattern. (c) In contrast, an acutely aversive dose of intra-VTA nicotine (0.008 nmol/0.5 μl) produces the opposite pattern of activity with decreased MSN activity and increased FSI activity. (d) However, pre-treatment with α-flu (0.8 mg/kg; i.p.) switches a normally ‘aversive' nicotine-related neuronal conditioning pattern into one similar to the acutely rewarding dose of intra-VTA nicotine. NAshell, shell region of the NAc.