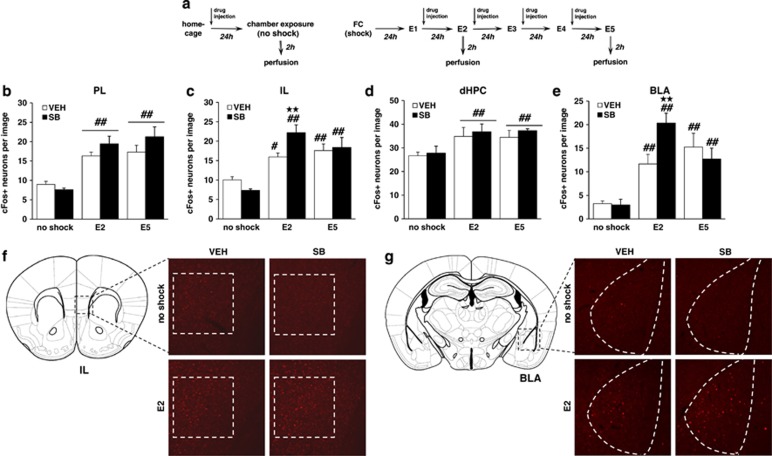
Figure 3.
The extinction-facilitating effects of Hcrtr-1 blockade are associated with an increased activity of the infralimbic prefrontal cortex and the basolateral amygdala. (a) Schematic representation of the experimental design for (b–g) biochemical experiments. (b–e) Number of neurons expressing cFos in the (b) PL, (c) IL, (d) dHPC, and (e) BLA of mice exposed to the context without receiving footshock, and mice subjected to FC and subsequent extinction until E2 and E5, treated with SB334867 (5 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle immediately after each extinction session (n=5–8 mice per group). (f and g) Schematic representation of the anatomic location of (f) IL (bregma +1.54 mm) and (g) BLA (bregma—1.58 mm) pictures adapted from Paxinos and Franklin's stereotaxic atlas (Paxinos and Franklin, 2001), and representative images of both regions obtained via fluorescence microscopy after direct labeling with rabbit polyclonal antiserum to cFos. Only no-shock and E2 groups are represented. Quantified areas appear delimited by a discontinuous line. Data are expressed as mean±SEM. **p<0.01 compared with the vehicle group; #p<0.05, ##p<0.01 compared with the no-shock group. FC, fear conditioning; E1–E5, extinction trials 1–5; VEH, vehicle; SB, SB334867; TCS, TCSOX229; PL, prelimbic prefrontal cortex; IL, infralimbic prefrontal cortex; dHPC, dorsal hippocampus; BLA, basolateral amygdala. A full color version of this figure is available at the Neuropsychopharmacology journal online.