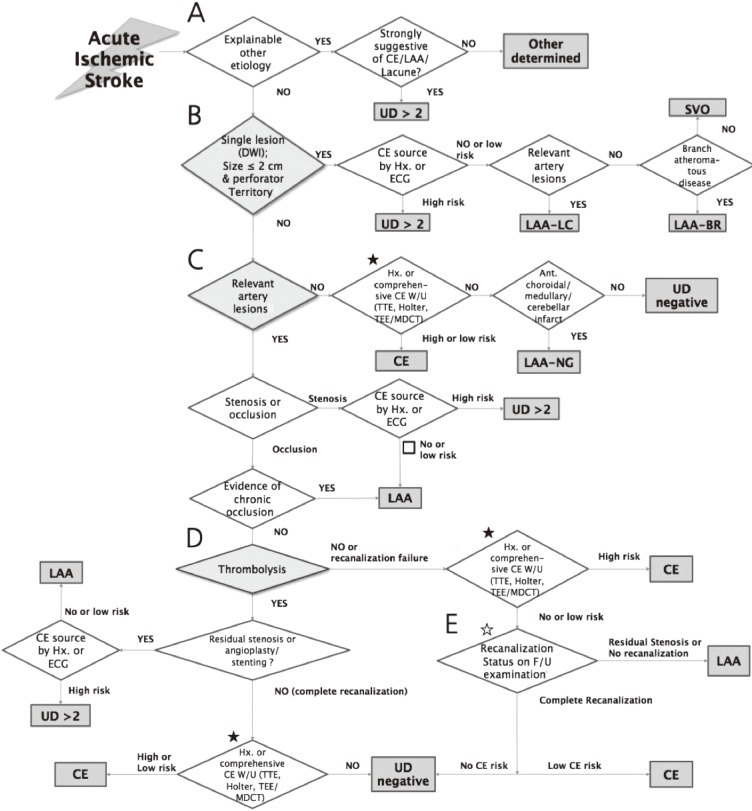
Figure 1.
MRI-based algorithm for acute ischemic stroke classification (MAGIC) (A) Step 1: Consideration of other determined etiology of stroke. (B) Step 2: Screening for small vessel occlusion (SVO) using MRI. (C) Step 3: Consideration of relevant artery stenosis or occlusion. (D) Step 4: Consideration of recanalization status of occluded artery after thrombolytic therapy. (E) Step 5: Consideration of follow-up recanalization status of occluded artery without thrombolytic therapy. ★: If one of three examinations (TTE, Holter, and TEE [or MDCT]) was not performed, then the patient was classified as 'undetermined incomplete'. ☆: The follow-up vascular status would be evaluated by MR/CT angiography or transcranial doppler (TCD). If no examinations are performed, then the patient should be classified as 'undetermined incomplete'. LAA, large artery atherosclerosis; SVO, small vessel occlusion; CE, cardioembolism; UD, undetermined cause; UD ≥2, two or more undetermined causes; DWI, diffusion weighted image; Hx, history; ECG, electrocardiography; LAA-LC, large artery atherosclerosis with lacunae; LAA-BR, branch atheromatous disease; W/U, work-up; TTE, transthoracic echocardiography; TEE, transesophageal echocardiography; MDCT, multi-detector row computerized tomography; Ant, Anterior; LAA-NG, large artery atherosclerosis with normal angiography; F/U, follow-up.